Molecular recognition and stabilization of iminium ions in water
- PMID: 17090022
- PMCID: PMC2562236
- DOI: 10.1021/ja0657915
Molecular recognition and stabilization of iminium ions in water
Abstract
Iminium ions are known to exist only transiently in aqueous solution due to their high reactivity toward hydrolysis. In this communication, we report on the generation and stabilization of iminium ions in aqueous solution via molecular encapsulation using a K12Ga4L6 host. Our studies revealed that tetrahedral host 1 can encapsulate a variety of iminium cations in a molecular recognition process that is selective based on the charge, hydrophobicity, size, and shape of the guest.
Figures
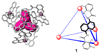

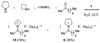
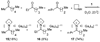
References
-
- Wong CH, Whitesides GM. Enzymes in Synthetic Organic Chemistry, Pergamon. Oxford: 1994.
- Jencks WP. Catalysis in Chemistry and Enzymology. New York: Dover; 1987.
-
- Bohme H, Haake M. In: Iminium Salts in Organic Chemistry; Advances in Organic Chemistry. Taylor EC, editor. New York: John Wiley and Sons; 1976. p. 145.
-
- Berkessel A, Gröger H. Asymmetric Organocatalysis: From Biomimetic Concepts to Applications in Asymmetric Synthesis. Wiley-VCH; 2005.
-
- Eldin S, Digits JA, Huang ST, Jencks WP. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995;117:6631.
-
- Vriezema DM, Aragones MC, Elemans J, Cornelissen J, Rowan AE, Nolte RJM. Chem. Rev. 2005;105:1445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

