A comparative analysis of genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation data for mammalian transcription factors
- PMID: 17090591
- PMCID: PMC1669715
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl803
A comparative analysis of genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation data for mammalian transcription factors
Abstract
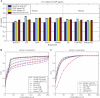
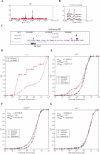
Genome-wide location analysis (ChIP-chip, ChIP-PET) is a powerful technique to study mammalian transcriptional regulation. In order to obtain a basic understanding of the location data generated for mammalian transcription factors and potential issues in their analysis, we conducted a comparative study of eight independent ChIP experiments involving six different transcription factors in human and mouse. Our cross-study comparisons, to the best of our knowledge the first to analyze multiple datasets, revealed the importance of carefully chosen genomic controls in the de novo identification of key transcription factor binding motifs, raised issues about the interpretation of ubiquitously occurring sequence motifs, and demonstrated the clustering tendency of protein-binding regions for certain transcription factors.
Figures


References
-
- Carroll J.S., Liu X.S., Brodsky A.S., Li W., Meyer C.A., Szary A.J., Eeckhoute J., Shao W., Hestermann E.V., Geistlinger T.R., et al. Chromosome-wide mapping of estrogen receptor binding reveals long-range regulation requiring the forkhead protein FoxA1. Cell. 2005;122:33–43. - PubMed
-
- Wei C.L., Wu Q., Vega V.B., Chiu K.P., Ng P., Zhang T., Shahab A., Yong H.C., Fu Y., Weng Z., et al. A global map of p53 transcription-factor binding sites in the human genome. Cell. 2006;124:207–219. - PubMed
-
- Loh Y.H., Wu Q., Chew J.L., Vega V.B., Zhang W., Chen X., Bourque G., George J., Leong B., Liu J., et al. The Oct4 and Nanog transcription network regulates pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nature Genet. 2006;38:431–440. - PubMed
-
- Liu X.S., Brutlag D.L., Liu J.S. An algorithm for finding protein-DNA binding sites with applications to chromatin-immunoprecipitation microarray experiments. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002;20:835–839. - PubMed

