Beta common receptor inactivation attenuates myeloproliferative disease in Nf1 mutant mice
- PMID: 17090653
- PMCID: PMC1794059
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-05-025395
Beta common receptor inactivation attenuates myeloproliferative disease in Nf1 mutant mice
Abstract
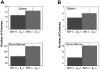
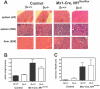
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) syndrome is caused by germline mutations in the NF1 tumor suppressor, which encodes neurofibromin, a GTPase activating protein for Ras. Children with NF1 are predisposed to juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML) and lethally irradiated mice given transplants with homozygous Nf1 mutant (Nf1-/-) hematopoietic stem cells develop a fatal myeloproliferative disorder (MPD) that models JMML. We investigated the requirement for signaling through the GM-CSF receptor to initiate and sustain this MPD by generating Nf1 mutant hematopoietic cells lacking the common beta chain (Beta c) of the GM-CSF receptor. Mice reconstituted with Nf1-/-, beta c-/- stem cells did not develop evidence of MPD despite the presence of increased number of immature hematopoietic progenitors in the bone marrow. Interestingly, when the Mx1-Cre transgene was used to inactivate a conditional Nf1 mutant allele in hematopoietic cells, concomitant loss of beta c-/- reduced the severity of the MPD, but did not abrogate it. Whereas inhibiting GM-CSF signaling may be of therapeutic benefit in JMML, our data also demonstrate aberrant proliferation of Nf1-/-myeloid progenitors that is independent of signaling through the GM-CSF receptor.
Figures



References
-
- Hope DG, Mulvihill JJ. Malignancy in neurofibromatosis. Adv Neurol. 1981;29:33–56. - PubMed
-
- Emanuel PD, Shannon KM, Castleberry RP. Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia: molecular understanding and prospects for therapy. Mol Med Today. 1996;2:468–475. - PubMed
-
- Arceci RJ, Longley BJ, Emanuel PD. Atypical cellular disorders. Hematology (Am Soc Hematol Educ Program) 2002:297–314. - PubMed
-
- Xu G, O'Connell P, Viskochil D, et al. The neurofibromatosis type 1 gene encodes a protein related to GAP. Cell. 1990;62:599–608. - PubMed
-
- DeClue JE, Papageorge AG, Fletcher JA, et al. Abnormal regulation of mammalian p21ras contributes to malignant tumor growth in von Recklinghausen (type 1) neurofibromatosis. Cell. 1992;69:265–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

