Correlation between beta cell mass and glycemic control in type 1 diabetic recipients of islet cell graft
- PMID: 17090674
- PMCID: PMC1859948
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0608141103
Correlation between beta cell mass and glycemic control in type 1 diabetic recipients of islet cell graft
Abstract
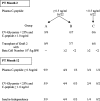
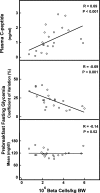
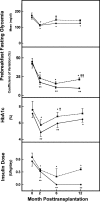
Islet grafts can induce insulin independence in type 1 diabetic patients, but their function is variable with only 10% insulin independence after 5 years. We investigated whether cultured grafts with defined beta cell number help standardize metabolic outcome. Nonuremic C-peptide-negative patients received an intraportal graft with 0.5-5.0 x 10(6) beta cells per kilogram of body weight (kg BW) under antithymocyte globulin and mycophenolate mofetil plus tacrolimus. Metabolic outcome at posttransplant (PT) month 2 was used to decide on a second graft under maintenance mycophenolate mofetil/tacrolimus. Graft function was defined by C-peptide >0.5 ng/ml and reduced insulin needs, metabolic control by reductions in HbA(1c), glycemia coefficient of variation, and hypoglycemia. At PT month 2, graft function was present in 16 of 17 recipients of >2 x 10(6) beta cells per kg BW versus 0 of 5 with lower number. The nine patients with C-peptide >1 ng/ml and glycemia coefficient of variation of <25% did not receive a second graft; five of them were insulin-independent until PT month 12. The 12 others received a second implant; it achieved insulin-independence at PT month 12 when the first and second graft contained >2 x 10(6) beta cells per kg BW. Of the 20 recipients of at least one graft with >2 x 10(6) beta cells per kg BW, 17 maintained graft function and metabolic control up to PT month 12. At PT month 12, beta cell function in insulin-independent patients ranged around 25% of age-matched control values. Thus, 1-year metabolic control can be reproducibly achieved and standardized by cultured islet cell grafts with defined beta cell number.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Robertson RP. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:694–705. - PubMed
-
- Hering BJ, Kandaswamy R, Ansite JD, Eckman PM, Nakano M, Sawada T, Matsumoto I, Ihm SH, Zhang HJ, Parky J, et al. J Am Med Assoc. 2005;293:830–835. - PubMed
-
- Hering BJ, Kandaswamy R, Harmon JV, Ansite JD, Clemmings SM, Sakai T, Paraskevas S, Eckman PM, Sageshima J, et al. Am J Transplant. 2004;4:390–401. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, Korbutt GS, Toth E, Warnock GL, Kneteman NM, Rajotte RV. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:230–238. - PubMed
-
- Ryan EA, Lakey JR, Paty BW, Imes S, Korbutt GS, Kneteman NM, Bigam D, Rajotte RV, Shapiro AM. Diabetes. 2002;51:2148–2157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

