Gene transfer in humans using a conditionally replicating lentiviral vector
- PMID: 17090675
- PMCID: PMC1635018
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0608138103
Gene transfer in humans using a conditionally replicating lentiviral vector
Abstract
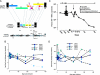
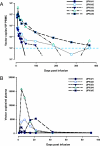
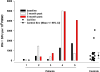
We report findings from a clinical evaluation of lentiviral vectors in a phase I open-label nonrandomized clinical trial for HIV. This trial evaluated the safety of a conditionally replicating HIV-1-derived vector expressing an antisense gene against the HIV envelope. Five subjects with chronic HIV infection who had failed to respond to at least two antiviral regimens were enrolled. A single i.v. infusion of gene-modified autologous CD4 T cells was well tolerated in all patients. Viral loads were stable, and one subject exhibited a sustained decrease in viral load. CD4 counts remained steady or increased in four subjects, and sustained gene transfer was observed. Self-limiting mobilization of the vector was observed in four of five patients. There is no evidence for insertional mutagenesis after 21-36 months of observation. Immune function improved in four subjects. Lentiviral vectors appear promising for gene transfer to humans.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: L.M.H., T.R., X.L., G.K.B., V.S., F.L., and B.D. were employees of VIRxSYS Corporation at the time this study was performed.
Figures
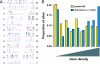
References
-
- Levine BL, Mosca J, Riley JL, Carroll RG, Vahey MT, Jagodizinski L, Wagner KF, Mayers DL, Burke DS, Weislow OS, et al. Science. 1996;272:1939–1943. - PubMed
-
- Lu X, Humeau L, Slepushkin V, Binder G, Yu Q, Slepushkina T, Chen Z, Merling R, Davis B, Chang YN, et al. J Gene Med. 2004;6:963–973. - PubMed
-
- Levine BL, Bernstein WB, Aronson NE, Schlienger K, Cotte J, Perfetto S, Humphries MJ, Ratto-Kim S, Birx DL, Steffans C, et al. Nat Med. 2002;8:47–53. - PubMed
-
- Humeau LM, Binder GK, Lu X, Slepushkin V, Merling R, Echeagaray P, Pereira M, Slepushkina T, Barnett S, Dropulic LK, et al. Mol Ther. 2004;9:902–913. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

