Harnessing a high cargo-capacity transposon for genetic applications in vertebrates
- PMID: 17096595
- PMCID: PMC1635535
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020169
Harnessing a high cargo-capacity transposon for genetic applications in vertebrates
Abstract
Viruses and transposons are efficient tools for permanently delivering foreign DNA into vertebrate genomes but exhibit diminished activity when cargo exceeds 8 kilobases (kb). This size restriction limits their molecular genetic and biotechnological utility, such as numerous therapeutically relevant genes that exceed 8 kb in size. Furthermore, a greater payload capacity vector would accommodate more sophisticated cis cargo designs to modulate the expression and mutagenic risk of these molecular therapeutics. We show that the Tol2 transposon can efficiently integrate DNA sequences larger than 10 kb into human cells. We characterize minimal sequences necessary for transposition (miniTol2) in vivo in zebrafish and in vitro in human cells. Both the 8.5-kb Tol2 transposon and 5.8-kb miniTol2 engineered elements readily function to revert the deficiency of fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase in an animal model of hereditary tyrosinemia type 1. Together, Tol2 provides a novel nonviral vector for the delivery of large genetic payloads for gene therapy and other transgenic applications.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. We note that the University of Minnesota and PBH, RSM, DAL, and SCE are all founders of a gene therapy company called Discovery Genomics, Incorporated.
Figures

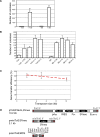
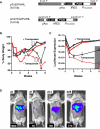
References
-
- Koga A, Hori H. The Tol2 transposable element of the medaka fish: An active DNA-based element naturally occurring in a vertebrate genome. Genes Genet Syst. 2001;76:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Koga A, Suzuki M, Inagaki H, Bessho Y, Hori H. Transposable element in fish. Nature. 1996;383:30. - PubMed
-
- Kawakami K, Koga A, Hori H, Shima A. Excision of the tol2 transposable element of the medaka fish, Oryzias latipes, in zebrafish, Danio rerio . Gene. 1998;225:17–22. - PubMed
-
- Ivics Z, Hackett PB, Plasterk RH, Izsvak Z. Molecular reconstruction of Sleeping Beauty, a Tc1-like transposon from fish, and its transposition in human cells. Cell. 1997;91:501–510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

