Bench-to-bedside review: thrombocytopenia-associated multiple organ failure--a newly appreciated syndrome in the critically ill
- PMID: 17096864
- PMCID: PMC1794442
- DOI: 10.1186/cc5064
Bench-to-bedside review: thrombocytopenia-associated multiple organ failure--a newly appreciated syndrome in the critically ill
Abstract
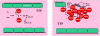
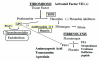
New onset thrombocytopenia and multiple organ failure (TAMOF) presages poor outcome in critical illness. Patients who resolve thrombocytopenia by day 14 are more likely to survive than those who do not. Patients with TAMOF have a spectrum of microangiopathic disorders that includes thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) and secondary thrombotic microanigiopathy (TMA). Activated protein C is effective in resolving fibrin-mediated thrombosis (DIC); however, daily plasma exchange is the therapy of choice for removing ADAMTS 13 inhibitors and replenishing ADAMTS 13 activity which in turn resolves platelet: von Willebrand Factor mediated thrombosis (TTP/secondary TMA).
Figures
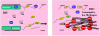

References
-
- Baughman RP, Lower EE, Flessa HC, Tollerud DJ. Thrombocytopenia in the intensive care unit. Chest. 1993;104:1243–1247. - PubMed
-
- Brun-Buisson C, Doyon F, Carlet J, Dellamonica P, Gouin F, Lepoutre A, Mercier JC, Offenstadt G, Regnier B. Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of severe sepsis and septic shock in adults. A multicenter prospective study in intensive care units. French ICU Group for Severe Sepsis. JAMA. 1995;274:968–974. doi: 10.1001/jama.274.12.968. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lee KH, Hui KP, Tan WC. Thrombocytopenia in sepsis: a predictor of mortality in the intensive care unit. Singapore Med J. 1993;34:245–246. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen TC, Han YY, Watson S, Carcillo JA, Kiss J. Thrombocytopenia is associated with multiple organ failure and death in children. Crit Care Med. 2000;28S:A50.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

