Nrf2-dependent protection from LPS induced inflammatory response and mortality by CDDO-Imidazolide
- PMID: 17097057
- PMCID: PMC2293275
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.102
Nrf2-dependent protection from LPS induced inflammatory response and mortality by CDDO-Imidazolide
Abstract
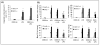
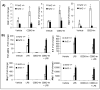
Sepsis induced lethality is characterized by amplified host innate immune response. Nrf2, a bZIP transcription factor, regulates a battery of cellular antioxidative genes and maintains cellular redox homeostasis. This study demonstrates that increasing Nrf2 activity by a potent small molecule activator, CDDO-Im (1-[2-cyano-3-,12-dioxooleana-1,9(11)-dien-28-oyl]imidazole), protects from deregulation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced innate immune response. In response to LPS stimuli, nrf2-deficient (nrf2 -/-) peritoneal neutrophils showed increased NADPH oxidase-dependent ROS generation, proinflammatory cytokines (Tnf-alpha and Il-6) and chemokines (Mip2 and Mcp-1) relative to wild-type (nrf2 +/+) cells. Pretreatment of peritoneal neutrophils with CDDO-Im induced antioxidative genes (Ho-1, Gclc, Gclm, and Nqo1) and attenuated LPS induced ROS generation as well as expression of proinflammatory cytokines exclusively in nrf2 +/+ neutrophils but not in nrf2 -/- cells. In corroboration with in vitro studies, pretreatment with CDDO-Im induced Nrf2-dependent antioxidative genes, attenuated LPS induced proinflammatory cytokine expression, and decreased mortality specifically in the nrf2 +/+ mice. In conclusion, the results suggest that Nrf2 is associated with oxidative regulation of LPS induced innate immune response in neutrophils. Activation of Nrf2-dependent compensatory antioxidative pathways by CDDO-Im protects from LPS induced inflammatory response and mortality.
Figures


References
-
- Cohen J. The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature. 2002;420:885–891. - PubMed
-
- Matsuzawa A, Saegusa K, Noguchi T, Sadamitsu C, Nishitoh H, Nagai S, Koyasu S, Matsumoto K, Takeda K, Ichijo H. ROS-dependent activation of the TRAF6-ASK1-p38 pathway is selectively required for TLR4-mediated innate immunity. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:587–592. - PubMed
-
- Nakahira K, Kim HP, Geng XH, Nakao A, Wang X, Murase N, Drain PF, Sasidhar M, Nabel EG, Takahashi T, Lukacs NW, Ryter SW, Morita K, Choi AM. Carbon monoxide differentially inhibits TLR signaling pathways by regulating ROS-induced trafficking of TLRs to lipid rafts. J Exp Med. 2006;203:2377–2389. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

