The role of intracellular signaling in insulin-mediated regulation of drug metabolizing enzyme gene and protein expression
- PMID: 17097148
- PMCID: PMC1828071
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2006.07.004
The role of intracellular signaling in insulin-mediated regulation of drug metabolizing enzyme gene and protein expression
Abstract
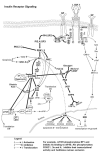
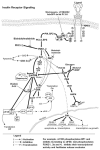
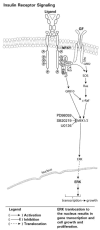
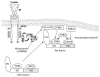
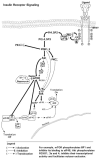
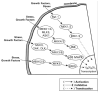
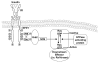
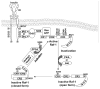
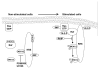
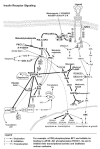
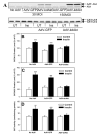
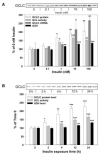
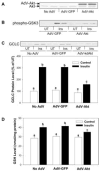
Endogenous factors, including hormones, growth factors and cytokines, play an important role in the regulation of hepatic drug metabolizing enzyme expression in both physiological and pathophysiological conditions. Diabetes, fasting, obesity, protein-calorie malnutrition and long-term alcohol consumption produce changes in hepatic drug metabolizing enzyme gene and protein expression. This difference in expression alters the metabolism of xenobiotics, including procarcinogens, carcinogens, toxicants and therapeutic agents, potentially impacting the efficacy and safety of therapeutic agents, and/or resulting in drug-drug interactions. Although the mechanisms by which xenobiotics regulate drug metabolizing enzymes have been studied intensively, less is known regarding the cellular signaling pathways and components which regulate drug metabolizing enzyme gene and protein expression in response to hormones and cytokines. Recent findings, however, have revealed that several cellular signaling pathways are involved in hormone- and growth factor-mediated regulation of drug metabolizing enzymes. Our laboratory has reported that insulin and growth factors regulate drug metabolizing enzyme gene and protein expression, including cytochromes P450 (CYP), glutathione S-transferases (GST) and microsomal epoxide hydrolase (mEH), through receptors which are members of the large receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family, and by downstream effectors such as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK), Akt/protein kinase B (PKB), mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and the p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase (p70S6 kinase). Here, we review current knowledge of the signaling pathways implicated in regulation of drug metabolizing enzyme gene and protein expression in response to insulin and growth factors, with the goal of increasing our understanding of how disease affects these signaling pathways, components, and ultimately gene expression and translational control.
Figures

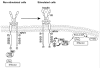
References
-
- Abdelmegeed MA, Carruthers NJ, Kim SK, Woodcroft KJ, Novak RF. Acetoacetate induces cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2E1 protein and suppresses CYP2E1 gene transcription in primary cultured rat hepatocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005;315:203–213. - PubMed
-
- Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Divoll M, Shader RI. Enhanced glucuronide conjugation of drugs in obesity: studies of lorazepam, oxazepam, and acetaminophen. J Lab Clin Med. 1983;101:873–880. - PubMed
-
- Agius C, Gidari AS. Effect of streptozotocin on the glutathione S-transferases of mouse liver cytosol. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985;34:811–819. - PubMed
-
- Alemzadeh R, Tushaus KM. Modulation of adipoinsular axis in prediabetic zucker diabetic fatty rats by diazoxide. Endocrinology. 2004;145:5476–84. - PubMed
-
- Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR. PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27489–27494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

