Tribbles homolog 2 inactivates C/EBPalpha and causes acute myelogenous leukemia
- PMID: 17097562
- PMCID: PMC2839500
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.09.012
Tribbles homolog 2 inactivates C/EBPalpha and causes acute myelogenous leukemia
Abstract
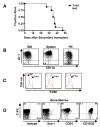
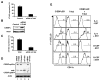
Tribbles homolog 2 (Trib2) was identified as a downregulated transcript in leukemic cells undergoing growth arrest. To investigate the effects of Trib2 in hematopoietic progenitors, mice were reconstituted with hematopoietic stem cells retrovirally expressing Trib2. Trib2-transduced bone marrow cells exhibited a growth advantage ex vivo and readily established factor-dependent cell lines. In vivo, Trib2-reconstituted mice uniformly developed fatal transplantable acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). In mechanistic studies, we found that Trib2 associated with and inhibited C/EBPalpha. Furthermore, Trib2 expression was elevated in a subset of human AML patient samples. Together, our data identify Trib2 as an oncogene that induces AML through a mechanism involving inactivation of C/EBPalpha.
Figures






References
-
- Akashi K, Traver D, Miyamoto T, Weissman IL. A clonogenic common myeloid progenitor that gives rise to all myeloid lineages. Nature. 2000;404:193–197. - PubMed
-
- Baer M, Johnson PF. Generation of truncated C/EBPbeta isoforms by in vitro proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:26582–26590. - PubMed
-
- Bisoffi M, Klima I, Gresko E, Durfee PN, Hines WC, Griffith JK, Studer UE, Thalmann GN. Expression profiles of androgen independent bone metastatic prostate cancer cells indicate up-regulation of the putative serine-threonine kinase GS3955. J Urol. 2004;172:1145–1150. - PubMed
-
- Bowers AJ, Scully S, Boylan JF. SKIP3, a novel Drosophila tribbles ortholog, is overexpressed in human tumors and is regulated by hypoxia. Oncogene. 2003;22:2823–2835. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

