Parkin is an E3 ubiquitin-ligase for normal and mutant ataxin-2 and prevents ataxin-2-induced cell death
- PMID: 17097639
- PMCID: PMC2788988
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.09.009
Parkin is an E3 ubiquitin-ligase for normal and mutant ataxin-2 and prevents ataxin-2-induced cell death
Abstract
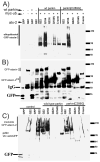
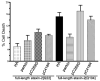
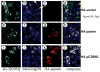
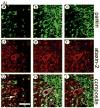
Expansion of the polyQ repeat in ataxin-2 results in degeneration of Purkinje neurons and other neuronal groups including the substantia nigra in patients with spinocerebellar ataxia type 2 (SCA2). In animal and cell models, overexpression of mutant ataxin-2 induces cell dysfunction and death, but little is known about steady-state levels of normal and mutant ataxin-2 and cellular mechanisms regulating their abundance. Based on preliminary findings that ataxin-2 interacted with parkin, an E3 ubiquitin ligase mutated in an autosomal recessive form of Parkinsonism, we sought to determine whether parkin played a role in regulating the steady-state levels of ataxin-2. Parkin interacted with the N-terminal half of normal and mutant ataxin-2, and ubiquitinated the full-length form of both wild-type and mutant ataxin-2. Parkin also regulated the steady-state levels of endogenous ataxin-2 in PC12 cells with regulatable parkin expression. Parkin reduced abnormalities in Golgi morphology induced by mutant ataxin-2 and decreased ataxin-2 induced cytotoxicity. In brains of SCA2 patients, parkin labeled cytoplasmic ataxin-2 aggregates in Purkinje neurons. These studies suggest a role for parkin in regulating the intracellular levels of both wild-type and mutant ataxin-2, and in rescuing cells from ataxin-2-induced cytotoxicity. The role of parkin variants in modifying the SCA2 phenotype and its use as a therapeutic target should be further investigated.
Figures





References
-
- Abbas N, Lucking CB, Ricard S, Durr A, Bonifati V, De Michele G, Bouley S, Vaughan JR, Gasser T, Marconi R, Broussolle E, Brefel-Courbon C, Harhangi BS, Oostra BA, Fabrizio E, Bohme GA, Pradier L, Wood NW, Filla A, Meco G, Denefle P, Agid Y, Brice A. A wide variety of mutations in the parkin gene are responsible for autosomal recessive parkinsonism in Europe. French Parkinson's Disease Genetics Study Group and the European Consortium on Genetic Susceptibility in Parkinson's Disease. Hum Mol Genet. 1999;8:567–574. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong J, Bonaventura I, Rojo A, Gonzalez G, Corral J, Nadal N, Volpini V, Ferrer I. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 2 (SCA2) with white matter involvement. Neurosci Lett. 2005;381:247–251. - PubMed
-
- Bingol B, Schuman EM. Activity-dependent dynamics and sequestration of proteasomes in dendritic spines. Nature. 2006;441:1144–1148. - PubMed
-
- Chung KK, Zhang Y, Lim KL, Tanaka Y, Huang H, Gao J, Ross CA, Dawson VL, Dawson TM. Parkin ubiquitinates the alpha-synuclein-interacting protein, synphilin-1: implications for Lewy-body formation in Parkinson disease. Nat Med. 2001;7:1144–1150. - PubMed
-
- Corti O, Hampe C, Koutnikova H, Darios F, Jacquier S, Prigent A, Robinson JC, Pradier L, Ruberg M, Mirande M, Hirsch E, Rooney T, Fournier A, Brice A. The p38 subunit of the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase complex is a Parkin substrate: linking protein biosynthesis and neurodegeneration. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12:1427–1437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

