Structure-based analysis of HU-DNA binding
- PMID: 17097674
- PMCID: PMC1945228
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.10.024
Structure-based analysis of HU-DNA binding
Abstract
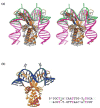
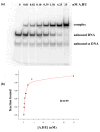
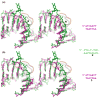
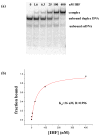
HU and IHF are prokaryotic proteins that induce very large bends in DNA. They are present in high concentrations in the bacterial nucleoid and aid in chromosomal compaction. They also function as regulatory cofactors in many processes, such as site-specific recombination and the initiation of replication and transcription. HU and IHF have become paradigms for understanding DNA bending and indirect readout of sequence. While IHF shows significant sequence specificity, HU binds preferentially to certain damaged or distorted DNAs. However, none of the structurally diverse HU substrates previously studied in vitro is identical with the distorted substrates in the recently published Anabaena HU(AHU)-DNA cocrystal structures. Here, we report binding affinities for AHU and the DNA in the cocrystal structures. The binding free energies for formation of these AHU-DNA complexes range from approximately 10-14.5 kcal/mol, representing K(d) values in the nanomolar to low picomolar range, and a maximum stabilization of at least approximately 6.3 kcal/mol relative to complexes with undistorted, non-specific DNA. We investigated IHF binding and found that appropriate structural distortions can greatly enhance its affinity. On the basis of the coupling of structural and relevant binding data, we estimate the amount of conformational strain in an IHF-mediated DNA kink that is relieved by a nick (at least 0.76 kcal/mol) and pinpoint the location of the strain. We show that AHU has a sequence preference for an A+T-rich region in the center of its DNA-binding site, correlating with an unusually narrow minor groove. This is similar to sequence preferences shown by the eukaryotic nucleosome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Flexible DNA bending in HU-DNA cocrystal structures.EMBO J. 2003 Jul 15;22(14):3749-60. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg351. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12853489 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and evolutionary analyses reveal determinants of DNA binding specificities of nucleoid-associated proteins HU and IHF.Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2017 Feb;107:356-366. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2016.11.014. Epub 2016 Nov 25. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2017. PMID: 27894997
-
Mutual stabilisation of bacteriophage Mu repressor and histone-like proteins in a nucleoprotein structure.J Mol Biol. 1995 Jun 2;249(2):332-41. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0300. J Mol Biol. 1995. PMID: 7783197
-
IHF and HU: flexible architects of bent DNA.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004 Feb;14(1):28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2003.12.003. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004. PMID: 15102446 Review.
-
DNA-protein interactions: IHF--the master bender.Curr Biol. 1997 Apr 1;7(4):R252-4. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00114-x. Curr Biol. 1997. PMID: 9162504 Review.
Cited by
-
The μ transpososome structure sheds light on DDE recombinase evolution.Nature. 2012 Nov 15;491(7424):413-7. doi: 10.1038/nature11602. Epub 2012 Nov 7. Nature. 2012. PMID: 23135398 Free PMC article.
-
H-NS mediates the dissociation of a refractory protein-DNA complex during Tn10/IS10 transposition.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Aug;39(15):6660-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr309. Epub 2011 May 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21565798 Free PMC article.
-
Making the bend: DNA tertiary structure and protein-DNA interactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Jul 14;15(7):12335-63. doi: 10.3390/ijms150712335. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25026169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shedding Light on Bacterial Chromosome Structure: Exploring the Significance of 3C-Based Approaches.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2819:3-26. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3930-6_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39028499 Review.
-
The Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron protein Bacteroides host factor A participates in integration of the integrative conjugative element CTnDOT into the chromosome.J Bacteriol. 2015 Apr;197(8):1339-49. doi: 10.1128/JB.02198-14. Epub 2015 Feb 2. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25645562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dame RT, Goosen N. HU: promoting or counteracting DNA compaction? FEBS Lett. 2002;529:151–6. - PubMed
-
- Arfin SM, Long AD, Ito ET, Tolleri L, Riehle MM, Paegle ES, Hatfield GW. Global gene expression profiling in Escherichia coli K12. The effects of integration host factor. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:29672–84. - PubMed
-
- Johnson RC, Johnson LM, Schmidt J, Garder JF. The major nucleoid proteins in the structure and function of the E. coli chromosome. In: Higgins NP, editor. Bacterial Chromosomes 1 edit. Vol. 1.1. American Society for Microbiology; 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

