Effect of novel nociceptin/orphanin FQ-NOP receptor ligands on ethanol drinking in alcohol-preferring msP rats
- PMID: 17097763
- PMCID: PMC1847604
- DOI: 10.1016/j.peptides.2006.09.007
Effect of novel nociceptin/orphanin FQ-NOP receptor ligands on ethanol drinking in alcohol-preferring msP rats
Abstract
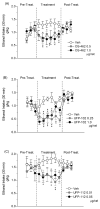
Activation of the NOP receptor by the endogenous ligand nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) reduces alcohol consumption in genetically selected alcohol-preferring Marchigian Sardinian (msP) rats. The present study evaluated the effect of three newly synthesized peptidergic and one brain-penetrating heterocyclic NOP receptor agonists on alcohol drinking in the two bottle choice paradigm. MsP rats were intracerebroventricularly (ICV) injected with the NOP receptor agonists OS-462 (0.5 and 1.0 microg), UFP-102 (0.25 and 1.0 microg) or UFP-112 (0.01 and 0.05 microg), or with Ro 64-6198 (0.3 and 1.0 mg/kg) given intraperitoneally (i.p.) and tested for 10% alcohol consumption. Results showed decreased alcohol consumption after treatment with all three peptidergic NOP receptor agonists (OS-462, UFP-102 and UFP-112). OS-462 (at the 1.0 microg dose) and UFP-102 (at the 0.25 microg dose) induced a significant increase in food intake as well. Surprisingly, Ro 64-6198 was ineffective at the 0.3 mg/kg dose, whereas it increased ethanol and food consumption at the 1.0 mg/kg dose. Pre-treatment with the selective mu-receptor antagonist naloxone (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.) reduced these effects of 1.0 mg/kg of Ro 64-6198. These findings confirm that activation of brain NOP receptors reduces alcohol drinking in msP rats and demonstrate that OS-462, UFP-102 and UFP-112 act as potent NOP receptor agonists. On the other hand, Ro 64-6198 increased alcohol drinking, an effect probably induced by a residual agonist activity of this compound at mu-opioid receptors. Overall, the results indicate that OS-462, UFP-102 and UFP-112 may represent valuable pharmacological tools to investigate the functional role of the brain N/OFQ system.
Figures

References
-
- Anton B, Fein J, To T, Li X, Silberstein L, Evans CJ. Immunohistochemical localization of ORL-1 in the central nervous system of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1996;368:229–351. - PubMed
-
- Chiou LC, Chuang KC, Wichmann J, Adam G. Ro 64-6198 [(1S,3aS)-8-(2,3,3a,4,5,6-Hexahydro-1H-phenalen-1-yl)-1-phenyl-1,3,8-triaza-spiro[4. 5]decan-4-one] acts differently from nociceptin/orphanin FQ in rat periaqueductal gray slices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;311:645–51. - PubMed
-
- Ciccocioppo R, Panocka I, Polidori C, Regoli D, Massi M. Effect of nociceptin on alcohol intake in alcohol-preferring rats. Psychopharmacology. 1999;141:220–4. - PubMed
-
- Ciccocioppo R, Angeletti S, Panocka I, Massi M. Nociceptin/orphanin FQ and drugs of abuse. Peptides. 2000;21:1071–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

