A membrane-bound NAC transcription factor regulates cell division in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 17098812
- PMCID: PMC1693948
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.106.043018
A membrane-bound NAC transcription factor regulates cell division in Arabidopsis
Abstract
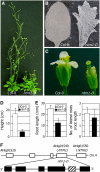
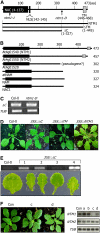
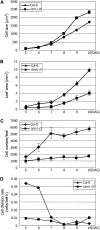
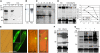
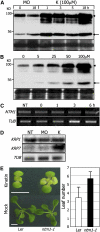
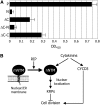
Controlled release of membrane-tethered, dormant precursors is an intriguing activation mechanism that regulates diverse cellular functions in eukaryotes. An exquisite example is the proteolytic activation of membrane-bound transcription factors. The proteolytic cleavage liberates active transcription factors from the membranes that can enter the nucleus and evokes rapid transcriptional responses to incoming stimuli. Here, we show that a membrane-bound NAC (for NAM, ATAF1/2, CUC2) transcription factor, designated NTM1 (for NAC with transmembrane motif1), is activated by proteolytic cleavage through regulated intramembrane proteolysis and mediates cytokinin signaling during cell division in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell proliferation was greatly reduced in an Arabidopsis mutant with retarded growth and serrated leaves in which a transcriptionally active NTM1 form was constitutively expressed. Accordingly, a subset of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor genes (the KIP-related proteins) was induced in this mutant with a significant reduction in histone H4 gene expression and in CDK activity. Consistent with a role for NTM1 in cell cycling, a Ds element insertional mutant was morphologically normal but displayed enhanced hypocotyl growth with accelerated cell division. Interestingly, cytokinins were found to regulate NTM1 activity by controlling its stability. These results indicate that the membrane-mediated activation of NTM1 defines a molecular mechanism by which cytokinin signaling is tightly regulated during cell cycling.
Figures


References
-
- Ahn, J., Kim, M., Lim, J.H., Kim, K.-T., and Pai, H.-S. (2004). Phytocalpain controls the proliferation and differentiation fates of cells in plant organ development. Plant J. 38 969–981. - PubMed
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000). Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408 796–815. - PubMed
-
- Brown, M.S., Ye, J., Rawson, R.B., and Goldstein, J.L. (2000). Regulated intramembrane proteolysis: A control mechanism conserved from bacteria to humans. Cell 100 391–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

