Concentration dependent selection of targets by an SR splicing regulator results in tissue-specific RNA processing
- PMID: 17098939
- PMCID: PMC1669769
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl755
Concentration dependent selection of targets by an SR splicing regulator results in tissue-specific RNA processing
Abstract
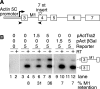
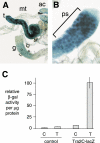
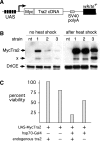
The splicing factor Transformer-2 (Tra2) is expressed almost ubiquitously in Drosophila adults, but participates in the tissue-specific regulation of splicing in several RNAs. In somatic tissues Tra2 participates in the activation of sex-specific splice sites in doublesex and fruitless pre-mRNAs. In the male germline it affects splicing of other transcripts and represses removal of the M1 intron from its own pre-mRNA. Here we test the hypothesis that the germline specificity of M1 repression is determined by tissue-specific differences in Tra2 concentration. We find that Tra2 is expressed at higher levels in primary spermatocytes of males than in other cell types. Increased Tra2 expression in other tissues reduces viability in a manner consistent with known dose-dependent effects of excessive Tra2 expression in the male germline. Somatic cells were found to be competent to repress M1 splicing if the level of Tra2 transcription was raised above endogenous concentrations. This suggests not only that M1 repression is restricted to the germline by a difference in Tra2 transcription levels but also that the protein's threshold concentration for M1 regulation differs from that of doublesex and fruitless RNAs. We propose that quantitative differences in regulator expression can give rise to cell-type-specific restrictions in splicing.
Figures
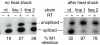

References
-
- Lopez A.J. Alternative splicing of pre-mRNA: developmental consequences and mechanisms of regulation. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1998;32:279–305. - PubMed
-
- Watermann D.O., Tang Y., Zur Hausen A., Jager M., Stamm S., Stickeler E. Splicing factor Tra2-beta1 is specifically induced in breast cancer and regulates alternative splicing of the CD44 gene. Cancer Res. 2006;66:4774–4780. - PubMed
-
- Hofmann Y., Wirth B. hnRNP-G promotes exon 7 inclusion of survival motor neuron (SMN) via direct interaction with Htra2-beta1. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002;11:2037–2049. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

