Evidence for immunological priming and increased frequency of CD4+ CD25+ cord blood T cells in children born to mothers with type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 17100770
- PMCID: PMC1810404
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03243.x
Evidence for immunological priming and increased frequency of CD4+ CD25+ cord blood T cells in children born to mothers with type 1 diabetes
Abstract
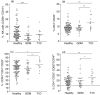
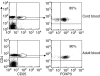
Maternal transmission of islet autoantibodies to children born to mothers with type 1 diabetes (T1D) has been shown to protect from autoantibodies and diabetes development later in life. However, the factors conferring disease protection are poorly understood. The aim of this study was to evaluate comparatively proinflammatory cytokines, autoantibodies and lymphocyte subsets in cord blood (CB) of children born to mothers with either T1D (n = 13), gestational diabetes (GDM) (n = 32) or healthy mothers (n = 81) in relation to transplacental passage of autoantibodies. The results are consistent with early priming of the fetal immune system only in children born to mothers with T1D. Levels of interleukin (IL)-1beta (P = 0.022), tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha (P = 0.002) and IL-8 (P = 0.0012), as well as the frequency of CD4(+) CD25(+) T cells (P < 0.01) were significantly increased, and the increased levels correlated positively with anti-GAD65 autoantibody (GADA) levels. Moreover, CD4(+) CD25(+) T cells of children born to T1D mothers exhibited a more pronounced memory phenotype with increased CCR4 expression and down-regulation of CD62L. These data suggest that early activation of the fetal immune system as a consequence of maternal autoimmunity and transplacental passage of GADA may influence the generation and expansion of fetal regulatory T cells. This might induce an early antigen-specific immunological tolerance that could protect against T1D later in life.
Figures
References
-
- Pociot F, McDermott MF. Genetics of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Genes Immun. 2002;3:235–49. - PubMed
-
- Itoh N, Hanafusa T, Miyazaki A, et al. Mononuclear cell infiltration and its relation to the expression of major histocompatibility complex antigens and adhesion molecules in pancreas biopsy specimens from newly diagnosed insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients. J Clin Invest. 1993;92:2313–22. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Peakman M, Wen L, McNab GL, Watkins PJ, Tan KC, Vergani D. T cell clones generated from patients with type 1 diabetes using interleukin-2 proliferate to human islet antigens. Autoimmunity. 1994;17:31–9. - PubMed
-
- Dahlquist GG, Ivarsson S, Lindberg B, Forsgren M. Maternal enteroviral infection during pregnancy as a risk factor for childhood IDDM. A population-based case-control study. Diabetes. 1995;44:408–13. - PubMed
-
- Dahlquist G, Blom L, Lonnberg G. The Swedish Childhood Diabetes Study – a multivariate analysis of risk determinants for diabetes in different age groups. Diabetologia. 1991;34:757–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

