Cytotoxic drug sensitivity of Epstein-Barr virus transformed lymphoblastoid B-cells
- PMID: 17101045
- PMCID: PMC1664586
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-265
Cytotoxic drug sensitivity of Epstein-Barr virus transformed lymphoblastoid B-cells
Abstract
Background: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is the causative agent of immunosuppression associated lymphoproliferations such as post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD), AIDS related immunoblastic lymphomas (ARL) and immunoblastic lymphomas in X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome (XLP). The reported overall mortality for PTLD often exceeds 50%. Reducing the immunosuppression in recipients of solid organ transplants (SOT) or using highly active antiretroviral therapy in AIDS patients leads to complete remission in 23-50% of the PTLD/ARL cases but will not suffice for recipients of bone marrow grafts. An additional therapeutic alternative is the treatment with anti-CD20 antibodies (Rituximab) or EBV-specific cytotoxic T-cells. Chemotherapy is used for the non-responding cases only as the second or third line of treatment. The most frequently used chemotherapy regimens originate from the non-Hodgkin lymphoma protocols and there are no cytotoxic drugs that have been specifically selected against EBV induced lymphoproliferative disorders.
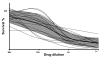
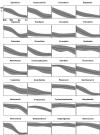
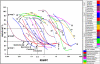
Methods: As lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) are well established in vitro models for PTLD, we have assessed 17 LCLs for cytotoxic drug sensitivity. After three days of incubation, live and dead cells were differentially stained using fluorescent dyes. The precise numbers of live and dead cells were determined using a custom designed automated laser confocal fluorescent microscope.
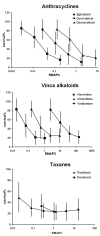
Results: Independently of their origin, LCLs showed very similar drug sensitivity patterns against 29 frequently used cytostatic drugs. LCLs were highly sensitive for vincristine, methotrexate, epirubicin and paclitaxel.
Conclusion: Our data shows that the inclusion of epirubicin and paclitaxel into chemotherapy protocols against PTLD may be justified.
Figures
References
-
- Leblond V, Sutton L, Dorent R, Davi F, Bitker MO, Gabarre J, Charlotte F, Ghoussoub JJ, Fourcade C, Fischer A, et al. Lymphoproliferative disorders after organ transplantation: a report of 24 cases observed in a single center. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:961–968. - PubMed
-
- Orazi A, Hromas RA, Neiman RS, Greiner TC, Lee CH, Rubin L, Haskins S, Heerema NA, Gharpure V, Abonour R, Srour EF, Cornetta K. Post transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders in bone marrow transplant recipients are aggressive diseases with a high incidence of adverse histologic and immunobiologic features. Am J Clin Pathol. 1997;107:419–429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

