The non-homologous end-joining protein Nej1p is a target of the DNA damage checkpoint
- PMID: 17101301
- PMCID: PMC3338008
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.09.010
The non-homologous end-joining protein Nej1p is a target of the DNA damage checkpoint
Abstract
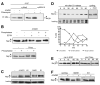
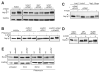
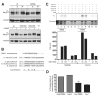
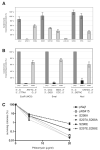
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), which are generated by ionizing radiation (IR) and a range of other DNA damaging agents, are repaired by homologous recombination (HR) or non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ). Previous studies have shown that NHEJ in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires the Yku70p-Yku80p heterodimer and a complex consisting of DNA Ligase IV, Lif1p and Nej1p. Here, we report that Nej1p is phosphorylated in response to DNA damage in a manner that relies on the DNA damage checkpoint kinases Mec1p, Rad53p and Dun1p. By using a mutational approach, we have identified a consensus Dun1p phosphorylation site in Nej1p, and mutation of conserved serine residues within it leads to decreased NHEJ efficiency. These data, together with previous findings that Rad55p--a protein involved in HR--is phosphorylated analogously, point to there being a broad signalling network connecting DNA damage checkpoint responses with the regulation of DNA DSB repair activities.
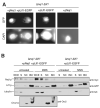
Figures
References
-
- Kolodner RD, Putnam CD, Myung K. Maintenance of genome stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 2002;297:552–557. - PubMed
-
- Rouse J, Jackson SP. Interfaces between the detection, signaling, and repair of DNA damage. Science. 2002;297:547–551. - PubMed
-
- Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Unsal-Kaccmaz K, Linn S. Molecular Mechanisms of Mammalian DNA Repair and the DNA Damage Checkpoints. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:39–85. - PubMed
-
- Melo J, Toczyski D. A unified view of the DNA-damage checkpoint. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 2002;14:237–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

