Distinct promoters mediate the regulation of Ebf1 gene expression by interleukin-7 and Pax5
- PMID: 17101802
- PMCID: PMC1800812
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01192-06
Distinct promoters mediate the regulation of Ebf1 gene expression by interleukin-7 and Pax5
Abstract
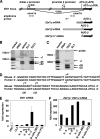
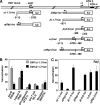
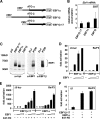
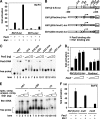
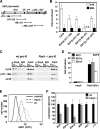
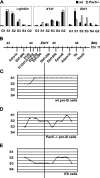
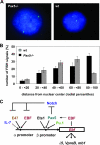
Early differentiation of B lymphocytes requires the function of multiple transcription factors that regulate the specification and commitment of the lineage. Loss- and gain-of-function experiments have provided important insight into the transcriptional control of B lymphopoiesis, whereby E2A was suggested to act upstream of EBF1 and Pax5 downstream of EBF1. However, this simple hierarchy cannot account for all observations, and our understanding of a presumed regulatory network, in which transcription factors and signaling pathways operate, is limited. Here, we show that the expression of the Ebf1 gene involves two promoters that are differentially regulated and generate distinct protein isoforms. We find that interleukin-7 signaling, E2A, and EBF1 activate the distal Ebf1 promoter, whereas Pax5, together with Ets1 and Pu.1, regulates the stronger proximal promoter. In the absence of Pax5, the function of the proximal Ebf1 promoter and accumulation of EBF1 protein are impaired and the replication timing and subcellular localization of the Ebf1 locus are altered. Taken together, these data suggest that the regulation of Ebf1 via distinct promoters allows for the generation of several feedback loops and the coordination of multiple determinants of B lymphopoiesis in a regulatory network.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptional function of E2A, Ebf1, Pax5, Ikaros and Aiolos analyzed by in vivo acute protein degradation in early B cell development.Nat Immunol. 2024 Sep;25(9):1663-1677. doi: 10.1038/s41590-024-01933-7. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Nat Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39179932
-
Coordinate regulation of B cell differentiation by the transcription factors EBF and E2A.Immunity. 1999 Jul;11(1):21-31. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80078-3. Immunity. 1999. PMID: 10435576
-
EBF1 and Pax5 safeguard leukemic transformation by limiting IL-7 signaling, Myc expression, and folate metabolism.Genes Dev. 2020 Nov 1;34(21-22):1503-1519. doi: 10.1101/gad.340216.120. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 33004416 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory network of B-cell differentiation: a focused view of early B-cell factor 1 function.Immunol Rev. 2014 Sep;261(1):102-15. doi: 10.1111/imr.12206. Immunol Rev. 2014. PMID: 25123279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B cell differentiation: role of E2A and Pax5/BSAP transcription factors.Oncogene. 1995 Aug 3;11(3):413-26. Oncogene. 1995. PMID: 7630627 Review.
Cited by
-
Compound haploinsufficiencies of Ebf1 and Runx1 genes impede B cell lineage progression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Apr 27;107(17):7869-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1003525107. Epub 2010 Apr 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20385820 Free PMC article.
-
Ezh2 Represses Transcription of Innate Lymphoid Genes in B Lymphocyte Progenitors and Maintains the B-2 Cell Fate.J Immunol. 2020 Apr 1;204(7):1760-1769. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901188. Epub 2020 Feb 24. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32094206 Free PMC article.
-
Orchestrating B cell lymphopoiesis through interplay of IL-7 receptor and pre-B cell receptor signalling.Nat Rev Immunol. 2014 Feb;14(2):69-80. doi: 10.1038/nri3570. Epub 2013 Dec 31. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24378843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The transcription repressors Bach2 and Bach1 promote B cell development by repressing the myeloid program.Nat Immunol. 2014 Dec;15(12):1171-80. doi: 10.1038/ni.3024. Epub 2014 Oct 26. Nat Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25344725
-
Ebf1 or Pax5 haploinsufficiency synergizes with STAT5 activation to initiate acute lymphoblastic leukemia.J Exp Med. 2011 Jun 6;208(6):1135-49. doi: 10.1084/jem.20101947. Epub 2011 May 23. J Exp Med. 2011. PMID: 21606506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arney, K. L., and A. G. Fisher. 2004. Epigenetic aspects of differentiation. J. Cell Sci. 117:4355-4363. - PubMed
-
- Azuara, V., K. E. Brown, R. R. Williams, N. Webb, N. Dillon, R. Festenstein, V. Buckle, M. Merkenschlager, and A. G. Fisher. 2003. Heritable gene silencing in lymphocytes delays chromatid resolution without affecting the timing of DNA replication. Nat. Cell Biol. 5:668-674. - PubMed
-
- Bain, G., E. C. Maandag, D. J. Izon, D. Amsen, A. M. Kruisbeek, B. C. Weintraub, I. Krop, M. S. Schlissel, A. J. Feeney, M. van Roon, et al. 1994. E2A proteins are required for proper B cell development and initiation of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. Cell 79:885-892. - PubMed
-
- Bertolino, E., K. Reddy, K. L. Medina, E. Parganas, J. Ihle, and H. Singh. 2005. Regulation of interleukin 7-dependent immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable gene rearrangements by transcription factor STAT5. Nat. Immunol. 6:836-843. - PubMed
-
- Chambeyron, S., N. R. Da Silva, K. A. Lawson, and W. A. Bickmore. 2005. Nuclear re-organisation of the Hoxb complex during mouse embryonic development. Development 132:2215-2223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
