Germ-line epigenetic modification of the murine A vy allele by nutritional supplementation
- PMID: 17101998
- PMCID: PMC1838538
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0607090103
Germ-line epigenetic modification of the murine A vy allele by nutritional supplementation
Abstract
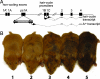
Environmental effects on phenotype can be mediated by epigenetic modifications. The epigenetic state of the murine A vy allele is highly variable, and determines phenotypic effects that vary in a mosaic spectrum that can be shifted by in utero exposure to methyl donor supplementation. We have asked if methyl donor supplementation affects the germ-line epigenetic state of the A vy allele. We find that the somatic epigenetic state of A vy is affected by in utero methyl donor supplementation only when the allele is paternally contributed. Exposure to methyl donor supplementation during midgestation shifts A vy phenotypes not only in the mice exposed as fetuses, but in their offspring. This finding indicates that methyl donors can change the epigenetic state of the A vy allele in the germ line, and that the altered state is retained through the epigenetic resetting that takes place in gametogenesis and embryogenesis. Thus a mother's diet may have an enduring influence on succeeding generations, independent of later changes in diet. Although other reports have suggested such heritable epigenetic changes, this study demonstrates that a specific mammalian gene can be subjected to germ-line epigenetic change.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
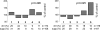

Comment in
-
Germ cells carry the epigenetic benefits of grandmother's diet.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov 14;103(46):17071-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608653103. Epub 2006 Nov 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17101997 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

