The minimum element of a synthetic peptide required to block prostate tumor cell migration
- PMID: 17102593
- PMCID: PMC2704570
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.5.11.3461
The minimum element of a synthetic peptide required to block prostate tumor cell migration
Abstract
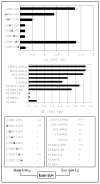
Human prostate tumor cell invasion and metastasis are dependent in part on cell adhesion to extracellular matrix proteins and cell migration. We previously identified a synthetic D-amino acid tumor cell adhesion peptide called HYD1 (kikmviswkg) that supported adhesion of tumor cells derived from breast, prostate, ovary and pancreas tissue. Alanine substitution analysis and a peptide deletion strategy were used to determine the minimal element of HYD1 necessary for bioactivity in a prostate cancer cell line called PC3N. Bioactivity was measured by assays of cell adhesion, migration and ERK signaling. The most potent element of HYD1 necessary to support cell adhesion was kmvixw, the block to migration required xkmviswxx and activation of ERK signaling required ikmviswxx. The shortest sequence active in all three assays was iswkg. The HYD1 peptide contains overlapping elements required for adhesion, blocking migration and the activation of ERK signaling. These linear peptide sequences provide the starting point for development of novel compounds to target cancer cell adhesion and migration.
Figures



Comment in
-
The chemokine receptor CXCR4: a homing device for hypoxic cancer cells?Cancer Biol Ther. 2006 Nov;5(11):1563-5. doi: 10.4161/cbt.5.11.3485. Epub 2006 Nov 14. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006. PMID: 17172811 No abstract available.
-
"D" approach to prevent metastasis.Cancer Biol Ther. 2007 Jan;6(1):110-1. doi: 10.4161/cbt.6.1.3786. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17264669 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Synthetic D-amino acid peptide inhibits tumor cell motility on laminin-5.Carcinogenesis. 2006 Sep;27(9):1748-57. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgl005. Epub 2006 Mar 14. Carcinogenesis. 2006. PMID: 16537560 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic peptides inhibit adhesion of human tumor cells to extracellular matrix proteins.Cancer Res. 2001 Apr 15;61(8):3308-13. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11309285
-
[Effects of Xihuang Pills on angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis of p rostate cancer based on FAK/Src/ERK pathway].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Dec;49(23):6378-6388. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240909.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39805784 Chinese.
-
Isoliquiritigenin inhibits migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells: possible mediation by decreased JNK/AP-1 signaling.J Nutr Biochem. 2009 Sep;20(9):663-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2008.06.005. Epub 2008 Sep 27. J Nutr Biochem. 2009. PMID: 18824345
-
Cell adhesion and tumor metastasis.Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1994;24:99-105. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1994. PMID: 8983067 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactivity improvement via display of the hydrophobic core of HYD1 in a cyclic β-hairpin-like scaffold, MTI-101.Pept Sci (Hoboken). 2021 May;113(3):e24199. doi: 10.1002/pep2.24199. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Pept Sci (Hoboken). 2021. PMID: 35859761 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis.Nature. 2015 Nov 19;527(7578):329-35. doi: 10.1038/nature15756. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26524530 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Effects of PEI-RGD/125I-(αv) ASODN on Growth and Invasion of HepG2 Cells.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Aug 10;21:2339-44. doi: 10.12659/MSM.893973. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26258995 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Laminin Binding Integrin Internalization in Prostate Cancer Cells.J Cell Biochem. 2017 May;118(5):1038-1049. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25673. Epub 2017 Jan 5. J Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 27509031 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical phenotype mixtures reveal advantages for tumor muscle invasion in vivo.Biophys J. 2023 Nov 7;122(21):4194-4206. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.09.016. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Biophys J. 2023. PMID: 37766428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chambers AF, MacDonald IC, Schmidt EE, Morris VL, Groom AC. Clinical targets for anti-metastasis therapy. Adv Cancer Res. 2000;79:91–121. - PubMed
-
- Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:563–72. - PubMed
-
- Kawaguchi T. Cancer metastasis: Characterization and identification of the behavior of metastatic tumor cells and the cell adhesion molecules, including carbohydrates. Curr Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord. 2005;5:39–64. - PubMed
-
- Okegawa T, Pong RC, Li Y, Hsieh JT. The role of cell adhesion molecule in cancer progression and its application in cancer therapy. Acta Biochim Pol. 2004;51:445–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
