Effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors on HIF-1
- PMID: 17102633
- PMCID: PMC4505804
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.5.21.3409
Effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors on HIF-1
Abstract
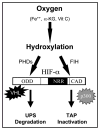
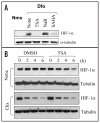
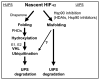
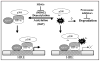
Hypoxia inducible factors (HIF) are the master transcriptional regulators of angiogenesis and energy metabolism in mammals. Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDAIs) are among the promising anti -cancer compounds currently in clinical trials. In addition to inducing hyperacetylation of histones, HDAIs have been found to repress HIF function, which has been construed as an important pharmacological mechanism underlying the HDAI -mediated repression of tumor growth and angiogenesis. While HDAIs are potent inhibitors of HIF function and thus may be useful in the prevention and treatment of cancers, a major dilemma is that they may induce hyperacetylation of nonspecific targets thus causing side effects. A better understanding is now required of the molecular and biochemical mechanisms underlying the anti -HIF effects of these compounds. Here we summarize the recent advances towards a better understanding of these molecular and biochemical mechanisms.
Figures

References
-
- Welsh SJ, Powis G. Hypoxia inducible factor as a cancer drug target. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2003;3:391–405. - PubMed
-
- Semenza GL. Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:721–32. - PubMed
-
- Giaccia A, Siim BG, Johnson RS. HIF-1 as a target for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:803–11. - PubMed
-
- Powis G, Kirkpatrick L. Hypoxia inducible factor-1α as a cancer drug target. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004;3:647–54. - PubMed
-
- Brown JM, Wilson WR. Exploiting tumour hypoxia in cancer treatment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:437–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
