Metabolic networks in motion: 13C-based flux analysis
- PMID: 17102807
- PMCID: PMC1682028
- DOI: 10.1038/msb4100109
Metabolic networks in motion: 13C-based flux analysis
Abstract
Many properties of complex networks cannot be understood from monitoring the components--not even when comprehensively monitoring all protein or metabolite concentrations--unless such information is connected and integrated through mathematical models. The reason is that static component concentrations, albeit extremely informative, do not contain functional information per se. The functional behavior of a network emerges only through the nonlinear gene, protein, and metabolite interactions across multiple metabolic and regulatory layers. I argue here that intracellular reaction rates are the functional end points of these interactions in metabolic networks, hence are highly relevant for systems biology. Methods for experimental determination of metabolic fluxes differ fundamentally from component concentration measurements; that is, intracellular reaction rates cannot be detected directly, but must be estimated through computer model-based interpretation of stable isotope patterns in products of metabolism.
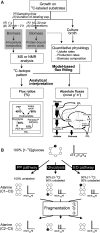
Figures


References
-
- Aderem A (2005) Systems biology: its practice and challenges. Cell 121: 511–513 - PubMed
-
- Almaas E, Kovacs B, Vicsek T, Oltavi ZN, Barabasi AL (2004) Global organization of metabolic fluxes in the bacterium Escherichia coli. Nature 427: 839–843 - PubMed
-
- Antoniewicz MR, Kelleher JK, Stephanopoulos G (2006) Determination of confidence intervals of metabolic fluxes estimated from stable isotope measurements. Metab Eng 8: 324–337 - PubMed
-
- Arauzo-Bravo MJ, Shimizu K (2003) An improved method for statistical analysis of metabolic flux analysis using isotopomer mapping matrices with analytical expression. J Biotechnol 105: 117–133 - PubMed
-
- Bacher A, Rieder C, Eichinger D, Arigoni D, Fuchs G, Eisenreich W (1999) Elucidation of novel biosynthetic pathways and metabolic flux patterns by retrobiosynthetic NMR analysis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 22: 567–598
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

