Thrombin-activatable procarboxypeptidase B regulates activated complement C5a in vivo
- PMID: 17105819
- PMCID: PMC1801069
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-03-012567
Thrombin-activatable procarboxypeptidase B regulates activated complement C5a in vivo
Erratum in
- Blood. 2007 May 1;109(9):3632. Piliposky, Adrian M [corrected to Piliponsky, Adrian M]
Abstract
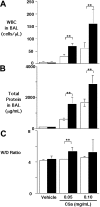
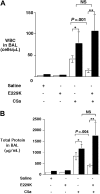
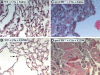
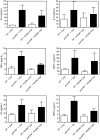
Plasma procarboxypeptidase B (proCPB) is activated by the endothelial thrombin-thrombomodulin [corrected] complex. Activated proCPB [corrected] (CPB) functions as a fibrinolysis inhibitor, but it may play a broader role by inactivating inflammatory mediators. To test this hypothesis, C5a-induced alveolitis was studied in wild-type (WT) and proCPB-deficient mice (proCPB-/-). C5a-induced alveolitis, as measured by cell counts and total protein contents in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids, was markedly enhanced in the proCPB-/- mice. E229K thrombin, a thrombin mutant with minimal clotting activity but retaining its ability to activate protein C and proCPB, attenuated C5a-induced alveolitis in WT but not in proCPB-/- mice, indicating that its beneficial effect is mediated primarily by its activation of proCPB. Lung tissue histology confirmed these cellular inflammatory responses. Delayed administration of E229K thrombin after the C5a instillation was ineffective in reducing alveolitis in WT mice, suggesting that the beneficial effect of E229K thrombin is due to the direct inhibition of C5a by CPB. Our studies show that thrombin-activatable proCPB, in addition to its role in fibrinolysis, has intrinsic anti-inflammatory functions. Its activation, along with protein C, by the endothelial thrombin-TM complex represents a homeostatic response to counteract the inflammatory mediators generated at the site of vascular injury.
Figures
References
-
- Walport MJ. Complement. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1058–1066. - PubMed
-
- Guo RF, Ward PA. Role of C5a in inflammatory responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:821–852. - PubMed
-
- Haviland DL, McCoy RL, Whitehead WT, et al. Cellular expression of the C5a anaphylatoxin receptor (C5aR): demonstration of C5aR on nonmyeloid cells of the liver and lung. J Immunol. 1995;154:1861–1869. - PubMed
-
- Schieferdecker HL, Schlaf G, Jungermann K, Gotze O. Functions of anaphylatoxin C5a in rat liver: direct and indirect actions on nonparenchymal and parenchymal cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2001;1:469–481. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

