Phase 2 study of an HIV-1 canarypox vaccine (vCP1452) alone and in combination with rgp120: negative results fail to trigger a phase 3 correlates trial
- PMID: 17106277
- PMCID: PMC2362395
- DOI: 10.1097/01.qai.0000248356.48501.ff
Phase 2 study of an HIV-1 canarypox vaccine (vCP1452) alone and in combination with rgp120: negative results fail to trigger a phase 3 correlates trial
Abstract
Background: A goal of T-cell HIV vaccines is to define the correlation between a vaccine-induced immune response and protection from HIV infection. We conducted a phase 2 trial to determine if a canarypox vaccine candidate (vCP1452) administered with rgp120 subunit protein would "qualify" for a trial to define a correlate of efficacy.
Methods: A total of 330 healthy volunteers were enrolled into 4 groups: 120 received vCP1452 alone (0, 1, 3, and 6 months), 120 received vCP1452 with 2 different regimens of rgp120 coadministration, and 90 received placebo. HIV-specific antibody responses were measured by enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) and neutralizing activity. T-cell responses were measured by chromium release and interferon-gamma (IFNgamma) enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISpot) assay.
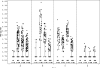
Results: Significant neutralizing antibody responses to the HIV MN strain were detected in all vaccine groups, with net responses ranging from 57% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 40% to 71%) to 94% (95% CI: 85% to 99%). Net cumulative HIV-specific CD8 IFNgamma ELISpot assay responses were 13% (95% CI: -1% to 26%) for recipients of vCP1452 alone and 16% (95% CI: 2% to 29%) for recipients of vCP1452 plus rgp120.
Conclusions: Overall, the HIV-specific CD8 cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) response was not sufficient to qualify the regimen for a subsequent trial designed to detect an immune correlate of protection requiring a minimum CD8 CTL frequency of 30%.
Figures
References
-
- Clements-Mann ML, Weinhold K, Matthews TJ, et al. Immune responses to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 induced by canarypox expressing HIV-1MN gp120, HIV-1SF2 recombinant gp120, or both vaccines in seronegative adults. NIAID AIDS Vaccine Evaluation Group. J Infect Dis. 1998;177:1230–1246. - PubMed
-
- Wright PF, Mestecky J, McElrath MJ, et al. Comparison of systemic and mucosal delivery of 2 canarypox virus vaccines expressing either HIV-1 genes or the gene for rabies virus G protein. J Infect Dis. 2004;189:1221–1231. - PubMed
-
- Gupta K, Hudgens M, Corey L, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a high-titered canarypox vaccine in combination with rgp120 in a diverse population of HIV-1–uninfected adults: AIDS Vaccine Evaluation Group Protocol 022A. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2002;29:254–261. - PubMed
-
- Evans TG, Keefer MC, Weinhold KJ, et al. A canarypox vaccine expressing multiple human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genes given alone or with rgp120 elicits broad and durable CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses in seronegative volunteers. J Infect Dis. 1999;180:290–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

