Crohn's disease: innate immunodeficiency?
- PMID: 17106921
- PMCID: PMC4087427
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i42.6751
Crohn's disease: innate immunodeficiency?
Abstract
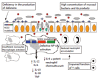
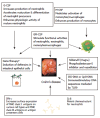
In the past, Crohn's disease (CD) has been understood primarily as an immunologic disorder characterized by an abnormal T-cell response. Recent in vitro and in vivo data suggests that CD may instead be precipitated by innate immune dysfunction resulting from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some reports have demonstrated a defective immune response in a variety of other cellular components, including neutrophils, monocytes and dendritic cells. Recent studies of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) in CD, aiming to stimulate the innate immune system with the conception that an innate immune defect underlies the development of the disease, have been demonstrated a clinical benefit and reinforce this evolving understanding of the disease.
Figures
References
-
- Ogura Y, Inohara N, Benito A, Chen FF, Yamaoka S, Nunez G. Nod2, a Nod1/Apaf-1 family member that is restricted to monocytes and activates NF-kappaB. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:4812–4818. - PubMed
-
- Inohara N, Ogura Y, Fontalba A, Gutierrez O, Pons F, Crespo J, Fukase K, Inamura S, Kusumoto S, Hashimoto M, et al. Host recognition of bacterial muramyl dipeptide mediated through NOD2. Implications for Crohn's disease. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:5509–5512. - PubMed
-
- Girardin SE, Boneca IG, Viala J, Chamaillard M, Labigne A, Thomas G, Philpott DJ, Sansonetti PJ. Nod2 is a general sensor of peptidoglycan through muramyl dipeptide (MDP) detection. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:8869–8872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

