Promoted differentiation of cynomolgus monkey ES cells into hepatocyte-like cells by co-culture with mouse fetal liver-derived cells
- PMID: 17106931
- PMCID: PMC4087437
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i42.6818
Promoted differentiation of cynomolgus monkey ES cells into hepatocyte-like cells by co-culture with mouse fetal liver-derived cells
Abstract
Aim: To explore whether a co-culture of cynomolgus monkey embryonic stem (cES) cells with embryonic liver cells could promote their differentiation into hepatocytes.
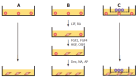
Methods: Mouse fetal liver-derived cells (MFLCs) were prepared as adherent cells from mouse embryos on embryonic d (ED) 14, after which undifferentiated cES cells were co-cultured with MFLCs. The induction of cES cells along a hepatic lineage was examined in MFLC-assisted differentiation, spontaneous differentiation, and growth factors (GF) and chemicals-induced differentiations (GF-induced differentiation) using retinoic acid, leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), FGF2, FGF4, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), oncostatin M (OSM), and dexamethasone.
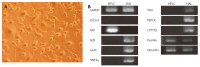
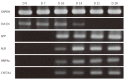
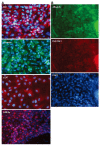
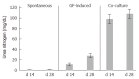
Results: The mRNA expression of alpha-fetoprotein, albumin (ALB), alpha-1-antitrypsin, and hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha was observed earlier in the differentiating cES cells co-cultured with MFLCs, as compared to cES cells undergoing spontaneous differentiation and those subjected to GF-induced differentiation. The expression of cytochrome P450 7a1, a possible marker for embryonic endoderm-derived mature hepatocytes, was only observed in cES cells that had differentiated in a co-culture with MFLCs. Further, the disappearance of Oct3/4, a representative marker of an undifferentiated state, was noted in cells co-cultured with MFLCs, but not in those undergoing spontaneous or GF-induced differentiation. Immunocytochemical analysis revealed an increased ratio of ALB-immunopositive cells among cES cells co-cultured with MFLCs, while glycogen storage and urea synthesis were also demonstrated.
Conclusion: MFLCs showed an ability to induce cES cells to differentiate toward hepatocytes. The co-culture system with MFLCs is a useful method for induction of hepatocyte-like cells from undifferentiated cES cells.
Figures


References
-
- Evans MJ, Kaufman MH. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature. 1981;292:154–156. - PubMed
-
- Shiroi A, Yoshikawa M, Yokota H, Fukui H, Ishizaka S, Tatsumi K, Takahashi Y. Identification of insulin-producing cells derived from embryonic stem cells by zinc-chelating dithizone. Stem Cells. 2002;20:284–292. - PubMed
-
- Yamada T, Yoshikawa M, Takaki M, Torihashi S, Kato Y, Nakajima Y, Ishizaka S, Tsunoda Y. In vitro functional gut-like organ formation from mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2002;20:41–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

