Identification of differentially expressed genes in mouse hepatocarcinoma ascites cell line with low potential of lymphogenous metastasis
- PMID: 17106944
- PMCID: PMC4087450
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i42.6893
Identification of differentially expressed genes in mouse hepatocarcinoma ascites cell line with low potential of lymphogenous metastasis
Abstract
Aim: To identify genes differentially expressed in mouse hepatocarcinoma ascites cell line with low potential of lymphogenous metastasis.
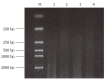
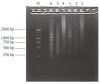
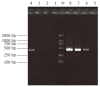
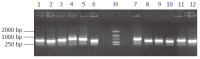
Methods: A subtracted cDNA library of mouse hepatocarcinoma cell line with low potential of lympho-genous metastasis Hca-P and its synogenetic cell line Hca-F with high metastatic potential was constructed by suppression subtracted hybridization (SSH) method. The screened clones of the subtracted library were sequenced and GenBank homology search was performed.
Results: Fifteen differentially expressed cDNA fragments of Hca-P were obtained which revealed 8 known genes, 4 expressed sequence tags (ESTs) and 3 cDNAs showed no homology.
Conclusion: Tumor metastasis is an incident involving multiple genes. SSH is a useful technique to detect differentially expressed genes and an effective method to clone novel genes.
Figures

References
-
- Diatchenko L, Lukyanov S, Lau YF, Siebert PD. Suppression subtractive hybridization: a versatile method for identifying differentially expressed genes. Methods Enzymol. 1999;303:349–380. - PubMed
-
- Karlseder J. Telomere repeat binding factors: keeping the ends in check. Cancer Lett. 2003;194:189–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

