Myofiber degeneration in autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (AD-EDMD) (LGMD1B)
- PMID: 17107595
- PMCID: PMC8095783
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2006.00028.x
Myofiber degeneration in autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (AD-EDMD) (LGMD1B)
Abstract
Autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy is caused by mutations in the LMNA gene that code for the nuclear membrane protein lamin A/C. We investigated skeletal muscle fibers from several muscles for cytoplasmic degenerative changes in three patients with genetically confirmed Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Methods included quantitative light and electron microscopy and PCR-based mutational analysis.
Results: The degenerative pathway was characterized by the gradual replacement of individual myofibers by connective tissue. Early stages of degeneration typically involved only a segment of the cross-sectional area of a myofiber. Intermediate stages consisted of myofiber shrinkage due to "shedding" of peripheral cytoplasmic portions into the endomysial space, and fragmentation of the myofibers by interposed collagen fibrils. Empty basement membrane sheaths surrounded by abundant deposits of extracellular matrix marked the end stage of the degenerative process. The nuclear number-to-cytoplasmic area in myofibers of one patient increased with increasing cross-sectional area, suggesting that satellite cell fusion with myofibers may have compensated for myofiber shrinkage. The pattern of degeneration described herein differs from muscular dystrophies with plasma membrane defects (dystrophinopathy, dysferlinopathy) and explains the frequently found absence of highly elevated serum creatine kinase levels in autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy.
Figures
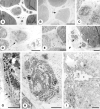
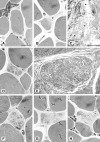

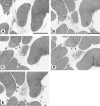

References
-
- Ben Yaou BR, Muchir A, Arimura T, Massart C, Demay L, Richard P, Bonne G (2005) Genetics of laminopathies. Novartis Found Symp 264:81–97. - PubMed
-
- Bonne G, Di Barletta MR, Varnous S, Becane HM, Hammouda EH, Merlini L, Muntoni F, Greenberg CR, Gary F, Urtizberea JA, Duboc D, Fardeau M, Toniolo D, Schwartz K (1999) Mutations in the gene encoding lamin A/C cause autosomal dominant Emery‐Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Nat Genet 21:285–288. - PubMed
-
- Bonne G, Mercuri E, Muchir A, Urtizberea A, Becane HM, Recan D, Merlini L, Wehnert M, Boor R, Reuner U, Vorgerd M, Wicklein EM, Eymard B, Duboc D, Penisson‐Besnier I, Cuisset JM, Ferrer X, Desguerre I, Lacombe D, Bushby K, Pollitt C, Toniolo D, Fardeau M, Schwartz K, Muntoni F (2000) Clinical and molecular genetic spectrum of autosomal dominant Emery‐Dreifuss muscular dystrophy due to mutations of the lamin A/C gene. Ann Neurol 48:170–180. - PubMed
-
- Bonne G, Ben Yaou RB, Beroud C, Boriani G, Brown S, De Visser M, Duboc D, Ellis J, Hausmanowa‐Petrusewicz I, Lattanzi G, Merlini L, Morris G, Muntoni F, Opolski G, Pinto YM, Sangiuolo F, Toniolo D, Trembath R, Van Berlo JH, Van der Kooi AJ, Wehnert M (2003) 108th ENMC International Workshop, 3rd Workshop of the MYO‐CLUSTER project EUROMEN, 7th International Emery‐Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy (EDMD) Workshop, 13–15 September 2002, Naarden, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul Disord 13:508–515. - PubMed
-
- Boriani G, Gallina M, Merlini L, Bonne G, Toniolo D, Amati S, Biffi M, Martignani C, Frabetti L, Bonvicini M, Rapezzi C, Branzi A (2003) Clinical relevance of atrial fibrillation/flutter, stroke, pacemaker implant, and heart failure in Emery‐Dreifuss muscular dystrophy: a long‐term longitudinal study. Stroke 2003:901–908. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

