Comparison of PrASE and Pyrosequencing for SNP Genotyping
- PMID: 17107626
- PMCID: PMC1657021
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-291
Comparison of PrASE and Pyrosequencing for SNP Genotyping
Abstract
Background: There is an imperative need for SNP genotyping technologies that are cost-effective per sample with retained high accuracy, throughput and flexibility. We have developed a microarray-based technique and compared it to Pyrosequencing. In the protease-mediated allele-specific extension (PrASE), the protease constrains the elongation reaction and thus prevents incorrect nucleotide incorporation to mismatched 3'-termini primers.
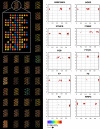
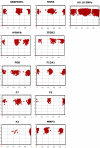
Results: The assay is automated for 48 genotyping reactions in parallel followed by a tag-microarray detection system. A script automatically visualizes the results in cluster diagrams and assigns the genotypes. Ten polymorphic positions suggested as prothrombotic genetic variations were analyzed with Pyrosequencing and PrASE technologies in 442 samples and 99.8 % concordance was achieved. In addition to accuracy, the robustness and reproducibility of the technique has been investigated.
Conclusion: The results of this study strongly indicate that the PrASE technology can offer significant improvements in terms of accuracy and robustness and thereof increased number of typeable SNPs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Competitive enzymatic reaction to control allele-specific extensions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Mar 14;33(5):e48. doi: 10.1093/nar/gni048. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15767273 Free PMC article.
-
SNPstream UHT: ultra-high throughput SNP genotyping for pharmacogenomics and drug discovery.Biotechniques. 2002 Jun;Suppl:70-2, 74, 76-7. Biotechniques. 2002. PMID: 12083401
-
Fluorescent microsphere-based readout technology for multiplexed human single nucleotide polymorphism analysis and bacterial identification.Hum Mutat. 2001 Apr;17(4):305-16. doi: 10.1002/humu.28. Hum Mutat. 2001. PMID: 11295829
-
Technologies for individual genotyping: detection of genetic polymorphisms in drug targets and disease genes.Am J Pharmacogenomics. 2002;2(3):197-205. Am J Pharmacogenomics. 2002. PMID: 12383026 Review.
-
Pyrosequencing: an accurate detection platform for single nucleotide polymorphisms.Hum Mutat. 2002 May;19(5):479-85. doi: 10.1002/humu.10078. Hum Mutat. 2002. PMID: 11968080 Review.
Cited by
-
Narrow genetic basis for the Australian dingo confirmed through analysis of paternal ancestry.Genetica. 2012 Mar;140(1-3):65-73. doi: 10.1007/s10709-012-9658-5. Epub 2012 May 23. Genetica. 2012. PMID: 22618967 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of common CYP1B1 mutations in Iranian POAG patients using a microarray-based PrASE protocol.Mol Vis. 2008;14:2349-56. Epub 2008 Dec 18. Mol Vis. 2008. PMID: 19096718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fan JB, Oliphant A, Shen R, Kermani BG, Garcia F, Gunderson KL, Hansen M, Steemers F, Butler SL, Deloukas P, Galver L, Hunt S, McBride C, Bibikova M, Rubano T, Chen J, Wickham E, Doucet D, Chang W, Campbell D, Zhang B, Kruglyak S, Bentley D, Haas J, Rigault P, Zhou L, Stuelpnagel J, Chee MS. Highly parallel SNP genotyping. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2003;68:69–78. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2003.68.69. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hardenbol P, Yu F, Belmont J, Mackenzie J, Bruckner C, Brundage T, Boudreau A, Chow S, Eberle J, Erbilgin A, Falkowski M, Fitzgerald R, Ghose S, Iartchouk O, Jain M, Karlin-Neumann G, Lu X, Miao X, Moore B, Moorhead M, Namsaraev E, Pasternak S, Prakash E, Tran K, Wang Z, Jones HB, Davis RW, Willis TD, Gibbs RA. Highly multiplexed molecular inversion probe genotyping: over 10,000 targeted SNPs genotyped in a single tube assay. Genome Res. 2005;15:269–275. doi: 10.1101/gr.3185605. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

