Efficacy of rituximab (anti-CD20) for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus involving the central nervous system
- PMID: 17107983
- PMCID: PMC1856059
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.057885
Efficacy of rituximab (anti-CD20) for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus involving the central nervous system
Abstract
Aim: Neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus (NPSLE) is a serious treatment-resistant phenotype of systemic lupus erythematosus. A standard treatment for NPSLE is not available. This report describes the clinical and laboratory tests of 10 patients with NPSLE before and after rituximab treatment, including changes in lymphocyte phenotypes.
Methods: Rituximab was administered at different doses in 10 patients with refractory NPSLE, despite intensive treatment.
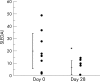
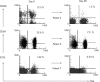
Results: Treatment with rituximab resulted in rapid improvement of central nervous system-related manifestations, particularly acute confusional state. Rituximab also improved cognitive dysfunction, psychosis and seizure, and reduced the SLE Disease Activity Index Score at day 28 in all 10 patients. These effects lasted for >1 year in five patients. Flow cytometric analysis showed that rituximab down regulated CD40 and CD80 on B cells and CD40L, CD69 and inducible costimulator on CD4+ T cells.
Conclusions: Rituximab rapidly improved refractory NPSLE, as evident by resolution of various clinical signs and symptoms and improvement of radiographic findings. The down regulation of functional molecules on B and T cells suggests that rituximab modulates the interaction of activated B and T cells through costimulatory molecules. These results warrant further analysis of rituximab as treatment for NPSLE.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of CD40 and CD80 on B cells in patients with life-threatening systemic lupus erythematosus after successful treatment with rituximab.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005 Feb;44(2):176-82. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh443. Epub 2004 Oct 19. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005. PMID: 15494350
-
Successful treatment with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (rituximab) of life-threatening refractory systemic lupus erythematosus with renal and central nervous system involvement.Lupus. 2003;12(10):798-800. doi: 10.1191/0961203303lu450xx. Lupus. 2003. PMID: 14596432 No abstract available.
-
Variability in the biological response to anti-CD20 B cell depletion in systemic lupus erythaematosus.Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 Dec;67(12):1724-31. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.083162. Epub 2008 Feb 4. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. PMID: 18250115 Clinical Trial.
-
[B cell targeting therapy using the anti-CD20 antibody in autoimmune diseases].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2009 Jun;129(6):675-9. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.129.675. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2009. PMID: 19483410 Review. Japanese.
-
Treatment of SLE with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody.Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2005;8:193-205. doi: 10.1159/000082104. Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2005. PMID: 15564722 Review.
Cited by
-
A combination of cellular biomarkers predicts failure to respond to rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis: a 24-week observational study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Aug 24;18(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1091-1. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27558631 Free PMC article.
-
B-cell-depletion therapy in SLE--what are the current prospects for its acceptance?Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009 Dec;5(12):711-6. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2009.218. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19946298 Review.
-
Rituximab in the treatment of severe lupus myelopathy.Clin Rheumatol. 2011 Jul;30(7):981-6. doi: 10.1007/s10067-011-1714-5. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Clin Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21340494 Clinical Trial.
-
Are lupus animal models useful for understanding and developing new therapies for human SLE?J Autoimmun. 2020 Aug;112:102490. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102490. Epub 2020 Jun 11. J Autoimmun. 2020. PMID: 32535128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CAR-T Cell Therapy: Advances in Kidney-Related Diseases.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2024 Jan 10;10(2):143-152. doi: 10.1159/000536194. eCollection 2024 Apr. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38751795 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kasitanon N, Louthrenoo W, Sukitawut W, Vichainun R. Causes of death and prognostic factors in Thai patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 20022085–91. - PubMed
-
- Hahn B H. Systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Kasper DL, ed. Origins of Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 16th edn. Columbus: McGraw‐Hill, 20051960–1967.
-
- Ad Hoc Working Group on Steroid‐Sparing Criteria in Lupus Criteria for steroid‐sparing ability of interventions in systemic lupus erythematosus: report of a consensus meeting. Arthritis Rheum 2004503427–3431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials