Cdk5 Modulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling regulates neuronal survival
- PMID: 17108320
- PMCID: PMC1783783
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e06-09-0851
Cdk5 Modulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling regulates neuronal survival
Abstract
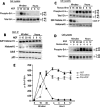
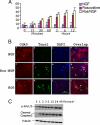
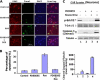
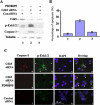
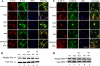
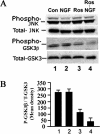
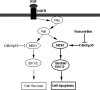
Cdk5, a cyclin-dependent kinase, is critical for neuronal development, neuronal migration, cortical lamination, and survival. Its survival role is based, in part, on "cross-talk" interactions with apoptotic and survival signaling pathways. Previously, we showed that Cdk5 phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK)1 inhibits transient activation induced by nerve growth factor (NGF) in PC12 cells. To further explore the nature of this inhibition, we studied the kinetics of NGF activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk)1/2 in cortical neurons with or without roscovitine, an inhibitor of Cdk5. NGF alone induced an Erk1/2-transient activation that peaked in 15 min and declined rapidly to baseline. Roscovitine, alone or with NGF, reached peak Erk1/2 activation in 30 min that was sustained for 48 h. Moreover, the sustained Erk1/2 activation induced apoptosis in cortical neurons. Significantly, pharmacological application of the MEK1 inhibitor PD98095 to roscovitine-treated cortical neurons prevented apoptosis. These results were also confirmed by knocking down Cdk5 activity in cortical neurons with Cdk5 small interference RNA. Apoptosis was correlated with a significant shift of phosphorylated tau and neurofilaments from axons to neuronal cell bodies. These results suggest that survival of cortical neurons is also dependent on tight Cdk5 modulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of tyrosine hydroxylase as a physiological substrate for Cdk5.J Neurochem. 2004 Oct;91(2):374-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02723.x. J Neurochem. 2004. PMID: 15447670 Free PMC article.
-
N-acetylcysteine prevents beta-amyloid toxicity by a stimulatory effect on p35/cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activity in cultured cortical neurons.J Neurosci Res. 2008 Sep;86(12):2685-95. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21710. J Neurosci Res. 2008. PMID: 18512759
-
Differential regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK1/2 and ERK5 by neurotrophins, neuronal activity, and cAMP in neurons.J Neurosci. 2001 Jan 15;21(2):434-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-02-00434.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11160424 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase 5: role in nervous system function and its specific inhibition by the Cdk5 inhibitory peptide.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Mar 11;1697(1-2):143-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2003.11.020. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15023357 Review.
-
Signaling pathways mediating anti-apoptotic action of neurotrophins.Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2000;60(4):531-45. doi: 10.55782/ane-2000-1374. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2000. PMID: 11200182 Review.
Cited by
-
Making a neuron: Cdk5 in embryonic and adult neurogenesis.Trends Neurosci. 2009 Nov;32(11):575-82. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2009.07.002. Epub 2009 Sep 24. Trends Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19782409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TFP5/TP5 peptide provides neuroprotection in the MPTP model of Parkinson's disease.Neural Regen Res. 2016 May;11(5):698-701. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.182681. Neural Regen Res. 2016. PMID: 27335538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclin I activates Cdk5 and regulates expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL in postmitotic mouse cells.J Clin Invest. 2009 Oct;119(10):3089-101. doi: 10.1172/JCI37978. Epub 2009 Sep 1. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19729834 Free PMC article.
-
6-Hydroxydopamine-induced PC12 cell death is mediated by MEF2D down-regulation.Neurochem Res. 2011 Feb;36(2):223-31. doi: 10.1007/s11064-010-0309-x. Epub 2010 Nov 6. Neurochem Res. 2011. PMID: 21057871
-
Altered expression of the Cdk5 activator-like protein, Cdk5α, causes neurodegeneration, in part by accelerating the rate of aging.Dis Model Mech. 2018 Mar 8;11(3):dmm031161. doi: 10.1242/dmm.031161. Dis Model Mech. 2018. PMID: 29469033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessandrini A., Brott B. K., Erikson R. L. Differential expression of MEK1 and MEK2 during mouse development. Cell Growth Differ. 1997;8:505–511. - PubMed
-
- Buee L., Bussiere T., Buee-Scherrer V., Delacourte A., Hof P. R. Tau protein isoforms, phosphorylation and role in neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 2000;33:95–130. - PubMed
-
- Cheung E. C., Slack R. S. Emerging role for ERK as a key regulator of neuronal apoptosis. Sci. STKE. 2004;2004:PE45. - PubMed
-
- Cheung Z. H., Ip N. Y. Cdk 5, mediator of neuronal death and survival. Neurosci. Lett. 2004;361:47–51. - PubMed
-
- Cheung Z. H., Fu A. K., Ip N. Y. Synaptic roles of Cdk5: implications in higher cognitive functions and neurodegenerative diseases. Neuron. 2006;50:13–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

