Role of FGF1, FGF2 and FGF7 in the development of the pancreas from control and streptozotocin-treated hamsters
- PMID: 17109637
- PMCID: PMC6496859
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2006.00410.x
Role of FGF1, FGF2 and FGF7 in the development of the pancreas from control and streptozotocin-treated hamsters
Abstract
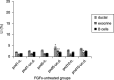
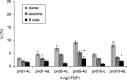
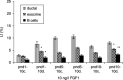
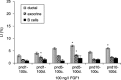
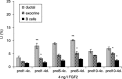
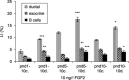
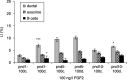
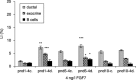
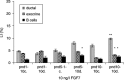
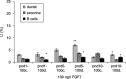
Although progress has been made with respect to the growth and transcription factors implicated in pancreatic development, many questions remain unsolved. It has been established that during embryonic life, both endocrine and acinar cells are derived from pancreatic epithelial precursor cells. Growth factors control the proliferation of precursor cells and their ability to differentiate into mature cells, both in pre-natal and in early post-natal life. Pancreatic development during the early post-natal period is an area of great interest for many scientists. In this study we have examined the structure characteristics, functional and proliferative activity of control and diabetic hamster pancreatic ductal, exocrine and beta cells, following treatment with FGFs 1, 2 and 7 in vitro. Light and electron microscopic studies indicated active synthetic processes in these cells under the influence of the investigated FGFs. In our experimental model of diabetes, the labelling index of the cells was significantly higher than in corresponding control groups of hamsters. We established that FGF2 at a concentration of 10 ng/l was responsible for the most prominent effect on ductal cells and beta cells in the diabetic groups. FGF1 at a concentration of 10 ng/l displayed the highest stimulatory effect on exocrine cells in the diabetic groups at post-natal day 10. Taken together these data strongly suggest that FGF1 and FGF2 induce proliferation of pancreatic epithelial cells during the early post-natal period whereas FGF7 is not strictly specific for pancreatic cell proliferation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of in vitro fibroblast growth factors on cell proliferation in pancreas from normal and streptozotocin-treated rats.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2002 Jul;57(1):11-6. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8227(02)00008-6. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2002. PMID: 12007725
-
Multiple fibroblast growth factors support growth of the ureteric bud but have different effects on branching morphogenesis.Mech Dev. 2001 Dec;109(2):123-35. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(01)00592-5. Mech Dev. 2001. PMID: 11731227
-
Fibroblast growth factor 2 promotes pancreatic epithelial cell proliferation via functional fibroblast growth factor receptors during embryonic life.Diabetes. 1998 Aug;47(8):1236-42. Diabetes. 1998. PMID: 9703323
-
In vivo cell transformation: neogenesis of beta cells from pancreatic ductal cells.Cell Transplant. 1995 Jul-Aug;4(4):371-83. doi: 10.1177/096368979500400408. Cell Transplant. 1995. PMID: 7582568 Review.
-
The ductal origin of structural and functional heterogeneity between pancreatic islets.Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2013 Oct;48(3):103-40. doi: 10.1016/j.proghi.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2013. PMID: 24100070 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of FGFR2b-ligand signaling on pancreatic branching morphogenesis and postnatal islet function.J Mol Histol. 2024 Dec 18;56(1):45. doi: 10.1007/s10735-024-10328-9. J Mol Histol. 2024. PMID: 39692915
-
Purified human pancreatic duct cell culture conditions defined by serum-free high-content growth factor screening.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33999. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033999. Epub 2012 Mar 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22442738 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Combinatorial Protein Microarray for Probing Materials Interaction with Pancreatic Islet Cell Populations.Microarrays (Basel). 2016 Aug 10;5(3):21. doi: 10.3390/microarrays5030021. Microarrays (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27600088 Free PMC article.
-
The Comparison of Adipose Stem Cell and Placental Stem Cell in Secretion Characteristics and in Facial Antiaging.Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:7315830. doi: 10.1155/2016/7315830. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Stem Cells Int. 2016. PMID: 27057176 Free PMC article.
-
FGF7 enhances the expression of ACE2 in human islet organoids aggravating SARS-CoV-2 infection.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Apr 23;9(1):104. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01790-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38654010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arany E, Hill DJ (2000) Ontogeny of fibroblast growth factors in the early development of the rat endocrine pancreas. Pediatr. Res. 48 (3), 389–403. - PubMed
-
- Bendayan M (1987) Presence of endocrine cells in pancreatic ducts. Pancreas 2 (4), 393–397. - PubMed
-
- Bonner‐Weir S, Smith FE (1994) Islet cell growth and the growth factors involved. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 5, 60–64. - PubMed
-
- Bonner‐Weir S, Trent DF, Honey RN, Weir GC (1981) Responses of neonatal rat islets to streptozotocin: limited B‐cell regeneration and hyperglycemia. Diabetes 30 (1), 64–69. - PubMed
-
- Bonner‐Weir S, Baxter LA, Schupin GT, Smith FA (1993) A second pathway for regeneration of adult exocrine and endocrine pancreas. Diabetes 42 (12), 1715–1720. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

