gamma-Tocotrienol inhibits ErbB3-dependent PI3K/Akt mitogenic signalling in neoplastic mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 17109639
- PMCID: PMC6496702
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2006.00412.x
gamma-Tocotrienol inhibits ErbB3-dependent PI3K/Akt mitogenic signalling in neoplastic mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
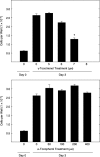
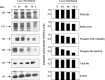
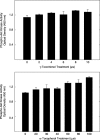
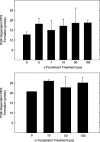
The antiproliferative effects of gamma-tocotrienol are associated with suppression in epidermal growth factor (EGF)-dependent phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/PI3K-dependent kinase-1 (PDK-1)/Akt mitogenic signalling in neoplastic mammary epithelial cells. Studies were conducted to investigate the direct effects of gamma-tocotrienol treatment on specific components within the PI3K/PDK-1/Akt mitogenic pathway. +SA cells were grown in culture and maintained in serum-free media containing 10 ng/ml EGF as a mitogen. Treatment with 0-8 microm gamma-tocotrienol resulted in a dose-responsive decrease in the +SA cell growth and a corresponding decrease in phospho-Akt (active) levels. However, gamma-tocotrienol treatment had no direct inhibitory effect on Akt or PI3K enzymatic activity, suggesting that the inhibitory effects of gamma-tocotrienol occur upstream of PI3K, possibly at the level of the EGF-receptor (ErbB1). Additional studies were conducted to determine the effects of gamma-tocotrienol on ErbB receptor activation. Results showed that gamma-tocotrienol treatment had little or no effect on ErbB1 or ErbB2 receptor tyrosine phosphorylation, a prerequisite for substrate interaction and signal transduction, but did cause a significant and progressive decrease in the ErbB3 tyrosine phosphorylation. Because ErbB1 or ErbB2 receptors form heterodimers with the ErbB3 receptor, and ErbB3 heterodimers have been shown to be the most potent activators of PI3K, these findings strongly suggest that the antiproliferative effects of gamma-tocotrienol in neoplastic +SA mouse mammary epithelial cells are mediated by a suppression in ErbB3-receptor tyrosine phosphorylation and subsequent reduction in PI3K/PDK-1/Akt mitogenic signalling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gamma-tocotrienol inhibits neoplastic mammary epithelial cell proliferation by decreasing Akt and nuclear factor kappaB activity.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2005 Apr;230(4):235-41. doi: 10.1177/153537020523000402. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2005. PMID: 15792944
-
Enhanced antiproliferative and apoptotic response to combined treatment of gamma-tocotrienol with erlotinib or gefitinib in mammary tumor cells.BMC Cancer. 2010 Mar 8;10:84. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-84. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20211018 Free PMC article.
-
Tocotrienol-induced caspase-8 activation is unrelated to death receptor apoptotic signaling in neoplastic mammary epithelial cells.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2004 Sep;229(8):745-55. doi: 10.1177/153537020422900806. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2004. PMID: 15337828
-
Tocotrienols target PI3K/Akt signaling in anti-breast cancer therapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013 Sep;13(7):1039-47. doi: 10.2174/18715206113139990116. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23272909 Review.
-
The ERBB3 receptor in cancer and cancer gene therapy.Cancer Gene Ther. 2008 Jul;15(7):413-48. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2008.15. Epub 2008 Apr 11. Cancer Gene Ther. 2008. PMID: 18404164 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tocotrienols Modulate a Life or Death Decision in Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 16;20(2):372. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020372. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30654580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beta-Tocotrienol Exhibits More Cytotoxic Effects than Gamma-Tocotrienol on Breast Cancer Cells by Promoting Apoptosis via a P53-Independent PI3-Kinase Dependent Pathway.Biomolecules. 2020 Apr 9;10(4):577. doi: 10.3390/biom10040577. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32283796 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic anticancer effects of combined γ-tocotrienol with statin or receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment.Genes Nutr. 2012 Jan;7(1):63-74. doi: 10.1007/s12263-011-0225-y. Epub 2011 May 1. Genes Nutr. 2012. PMID: 21533791 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-preventive activities of tocopherols and tocotrienols.Carcinogenesis. 2010 Apr;31(4):533-42. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp205. Epub 2009 Sep 11. Carcinogenesis. 2010. PMID: 19748925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges and Opportunities of Nanotechnology as Delivery Platform for Tocotrienols in Cancer Therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Nov 26;9:1358. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01358. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30534071 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson LW, Danielson KG, Hosick HL (1981) Metastatic potential of hyperplastic alveolar nodule derived mouse mammary tumor cells following intravenous inoculation. Eur. J. Cancer Clin. Oncol. 17, 1001–1008. - PubMed
-
- Bazley LA, Gullick WJ (2005) The epidermal growth factor receptor family. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 12 (Suppl. 1), S17–S27. - PubMed
-
- Britten CD (2004) Targeting ErbB receptor signaling: a pan‐ErbB approach to cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 3, 1335–1342. - PubMed
-
- Danielson KG, Anderson LW, Hosick HL (1980) Selection and characterization in culture of mammary tumor cells with distinctive growth properties in vivo. Cancer Res. 40, 1812–1819. - PubMed
-
- Downward J (1998) Mechanisms and consequences of activation of protein kinase B/Akt. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 10, 262–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

