Angiotensin II induces phosphorylation of glucose-regulated protein-75 in WB rat liver cells
- PMID: 17109810
- PMCID: PMC2577571
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2006.10.011
Angiotensin II induces phosphorylation of glucose-regulated protein-75 in WB rat liver cells
Abstract
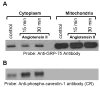
Studies in vascular smooth muscle cells suggest that, angiotensin II (Ang II)-mediated cellular response requires transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R), and involves tyrosine phosphorylation of caveolin-1. Here we demonstrate that, exposure of WB rat liver cells to Ang II does not cause transactivation of EGF-R, but did rapidly activate p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases suggesting that it activates MAP kinases independent of EGF-R transactivation. We observed that the phospho-specific anti-caveolin-1 antibody detected a tyrosine phosphorylated, 75kDa protein in Ang II-treated cells which we identified as glucose regulated protein-75 (GRP-75). Phosphoamino acid analysis showed that Ang II induced its phosphorylation at tyrosine, serine and threonine residues and was localized to the cytoplasm. The ability of Ang-II to induce GRP-75 phosphorylation suggests that it may play a role in the protection of cytoplasmic proteins from the damaging effect of oxidative stress known to be produced during Ang-II induced signaling.
Figures




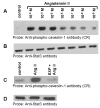
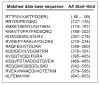



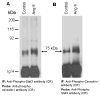
References
-
- Kim S, Iwao H. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52:11–34. - PubMed
-
- Touz RM, Schiffrin EL. Pharmcol Rev. 2000;52:639–672. - PubMed
-
- Marshal RP, Gohlke P, Chambers RC, Howell DC, Bottoms SE, Unger T, McAnulty RJ, Laurent GJ. Am J Phyiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004;286:156–164. - PubMed
-
- Guo G, Morrissey J, McCracken R, Tolley T, Liapis H, Klahr S. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001;280:F777–F785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

