Angiotensin II induces IL-6 expression and the Jak-STAT3 pathway in aortic adventitia of LDL receptor-deficient mice
- PMID: 17109863
- PMCID: PMC2196437
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.10.013
Angiotensin II induces IL-6 expression and the Jak-STAT3 pathway in aortic adventitia of LDL receptor-deficient mice
Abstract
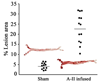
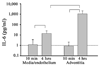
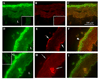
Angiotensin II (A-II), the major effector peptide of the renin angiotensin system potently accelerates progression of atherosclerosis. To investigate its effects on vascular inflammatory mechanisms, we elucidated vascular cytokine expression during early lesion development in A-II-infused atherosclerosis-prone LDLR-/- mice. Male LDLR-/- mice were placed on a "Western" high-fat diet for 4 weeks, followed by sham or A-II infusion for 7 weeks. Equal blood pressures and elevations in serum lipids were seen in both groups. Mice were sacrificed when significant A-II-induced plaque development was first detectable, aortae were explanted and culture media assayed for secreted cytokines. Nine cytokines were significantly induced with interleukin-6 (IL-6) being the most highly secreted. Local IL-6 production was confirmed by in situ mRNA hybridization and immunostaining, where the most abundant IL-6 was found in the aortic adventitia, with lesser production by the medial and intimal layers. Immunofluorescence colocalization showed IL-6 expression by fibroblasts and activated macrophages. Activation of downstream IL-6 signaling mediated by the Jak-STAT3 pathway was demonstrated by inducible phospho-Tyr705-STAT3 formation in the adventitia and endothelium (of IL-6+/+ mice only). These findings define cytokine profiles in the A-II infusion model and demonstrate that IL-6, produced by activated macrophages and fibroblasts in the adventitia, induces the Jak-STAT3 pathway during early A-II-induced atherosclerosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interleukin-6-signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 signaling mediates aortic dissections induced by angiotensin II via the T-helper lymphocyte 17-interleukin 17 axis in C57BL/6 mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Jul;33(7):1612-21. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.301049. Epub 2013 May 16. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23685554 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II activates JAK2/STAT3 pathway and induces interleukin-6 production in cultured rat brainstem astrocytes.Regul Pept. 2010 Jan 8;159(1-3):110-6. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2009.09.001. Regul Pept. 2010. PMID: 19748527
-
Osimertinib exacerbates immune checkpoint inhibitor-related severe adverse events by activating the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway in macrophages.Cancer Biol Med. 2024 Dec 9;21(12):1156-70. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0269. Cancer Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39651787 Free PMC article.
-
Krüppel-Like Factor 15/Interleukin 11 Axis-Mediated Adventitial Remodeling Depends on Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinases 1 and 2 Activation in Angiotensin II-Induced Hypertension.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Aug 17;10(16):e020554. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.020554. Epub 2021 Aug 5. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34350769 Free PMC article.
-
The IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway: potential therapeutic strategies in treating colorectal cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2014 Apr;44(4):1032-40. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2259. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24430672 Review.
Cited by
-
Small-molecule inhibitors of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 protect against angiotensin II-induced vascular dysfunction and hypertension.Hypertension. 2013 Feb;61(2):437-42. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.00299. Epub 2012 Dec 24. Hypertension. 2013. PMID: 23266544 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological agents modifying the renin angiotensin and natriuretic peptide systems in COVID-19 patients.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2021 Sep;133(17-18):983-988. doi: 10.1007/s00508-021-01855-6. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2021. PMID: 33877436 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effects of Vitamin D on the Renin-Angiotensin System and Acute Childhood Pneumonia.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Nov 3;11(11):1545. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11111545. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358201 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of an immune-related signature for predicting the ischemic events in patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 10;13:1014264. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1014264. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36299596 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory pathways in COVID-19: Mechanism and therapeutic interventions.MedComm (2020). 2022 Aug 1;3(3):e154. doi: 10.1002/mco2.154. eCollection 2022 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2022. PMID: 35923762 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Daugherty A, Cassis L. Angiotensin II-mediated development of vascular diseases. Trends in Cardiovasc Med. 2004;14:117–120. - PubMed
-
- Kon V, Jabs K. Angiotensin in atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2004;13:291–297. - PubMed
-
- Brasier AR, Recinos A, Eledrisi MS. Vascular inflammation and the renin-angiotensin system. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22:1257–1266. - PubMed
-
- Brasier AR, Jamaluddin M, Han Y, Patterson C, Runge MS. Angiotensin II induces gene transcription through cell-type-dependent effects on the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB)transcription factor. Mol Cell Biochem. 2000:155–699. - PubMed
-
- Murphy TJ, Alexander RW, Griendling KK, Runge MS, Bernstein KE. Isolation of a cDNA encoding the vascular type-1 angiotensin II receptor. Nature. 1991;351:233–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

