Kinetic analysis of GTP hydrolysis catalysed by the Arf1-GTP-ASAP1 complex
- PMID: 17112341
- PMCID: PMC1863566
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20061217
Kinetic analysis of GTP hydrolysis catalysed by the Arf1-GTP-ASAP1 complex
Erratum in
- Biochem J. 2007 Nov 1;407(3):471
Abstract
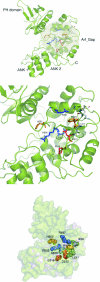
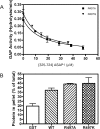
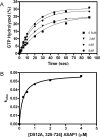
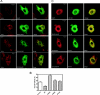
Arf (ADP-ribosylation factor) GAPs (GTPase-activating proteins) are enzymes that catalyse the hydrolysis of GTP bound to the small GTP-binding protein Arf. They have also been proposed to function as Arf effectors and oncogenes. We have set out to characterize the kinetics of the GAP-induced GTP hydrolysis using a truncated form of ASAP1 [Arf GAP with SH3 (Src homology 3) domain, ankyrin repeats and PH (pleckstrin homology) domains 1] as a model. We found that ASAP1 used Arf1-GTP as a substrate with a k(cat) of 57+/-5 s(-1) and a K(m) of 2.2+/-0.5 microM determined by steady-state kinetics and a kcat of 56+/-7 s(-1) determined by single-turnover kinetics. Tetrafluoroaluminate (AlF4-), which stabilizes complexes of other Ras family members with their cognate GAPs, also stabilized a complex of Arf1-GDP with ASAP1. As anticipated, mutation of Arg-497 to a lysine residue affected kcat to a much greater extent than K(m). Changing Trp-479, Iso-490, Arg-505, Leu-511 or Asp-512 was predicted, based on previous studies, to affect affinity for Arf1-GTP. Instead, these mutations primarily affected the k(cat). Mutants that lacked activity in vitro similarly lacked activity in an in vivo assay of ASAP1 function, the inhibition of dorsal ruffle formation. Our results support the conclusion that the Arf GAP ASAP1 functions in binary complex with Arf1-GTP to induce a transition state towards GTP hydrolysis. The results have led us to speculate that Arf1-GTP-ASAP1 undergoes a significant conformational change when transitioning from the ground to catalytically active state. The ramifications for the putative effector function of ASAP1 are discussed.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mutational analysis of the Arf1*GTP/Arf GAP interface reveals an Arf1 mutant that selectively affects the Arf GAP ASAP1.Curr Biol. 2005 Dec 6;15(23):2164-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.10.065. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16332543
-
Interaction of the N terminus of ADP-ribosylation factor with the PH domain of the GTPase-activating protein ASAP1 requires phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate.J Biol Chem. 2019 Nov 15;294(46):17354-17370. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009269. Epub 2019 Oct 6. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31591270 Free PMC article.
-
Differences between AGAP1, ASAP1 and Arf GAP1 in substrate recognition: interaction with the N-terminus of Arf1.Cell Signal. 2004 Sep;16(9):1033-44. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2004.02.008. Cell Signal. 2004. PMID: 15212764
-
Membrane curvature and the control of GTP hydrolysis in Arf1 during COPI vesicle formation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Aug;33(Pt 4):619-22. doi: 10.1042/BST0330619. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16042557 Review.
-
The role of ADP-ribosylation factor and SAR1 in vesicular trafficking in plants.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Jul 1;1664(1):9-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.04.005. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15238254 Review.
Cited by
-
Src-dependent phosphorylation of ASAP1 regulates podosomes.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Dec;27(23):8271-83. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01781-06. Epub 2007 Sep 24. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17893324 Free PMC article.
-
CAST AWAY, a membrane-associated receptor-like kinase, inhibits organ abscission in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2011 Aug;156(4):1837-50. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.175224. Epub 2011 May 31. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21628627 Free PMC article.
-
The ins and outs of the Arf4-based ciliary membrane-targeting complex.Small GTPases. 2021 Jan;12(1):1-12. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2019.1616355. Epub 2019 May 17. Small GTPases. 2021. PMID: 31068062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allele-Specific Interactions between CAST AWAY and NEVERSHED Control Abscission in Arabidopsis Flowers.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Oct 21;7:1588. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01588. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27818674 Free PMC article.
-
A PH domain in the Arf GTPase-activating protein (GAP) ARAP1 binds phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate and regulates Arf GAP activity independently of recruitment to the plasma membranes.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 9;284(41):28069-28083. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.028266. Epub 2009 Aug 7. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19666464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cukierman E., Huber I., Rotman M., Cassel D. The ARF1 GTPase-activating protein – zinc-finger motif and Golgi complex localization. Science. 1995;270:1999–2002. - PubMed
-
- Randazzo P. A., Hirsch D. S. Arf GAPs: multifunctional proteins that regulate membrane traffic and actin remodelling. Cell. Signalling. 2004;16:401–413. - PubMed
-
- Schmalzigang R., Premont R. T. GIT proteins: Arf GAPs and signaling scaffolds. In: Kahn R. A., editor. Arf Family GTPases. Dordrecht: Kluwer; 2003. pp. 159–184.
-
- Turner C. E., West K. A., Brown M. C. Paxillin-ARF GAP signaling and the cytoskeleton. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2001;13:593–599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

