HIV-1 immunopathogenesis: how good interferon turns bad
- PMID: 17112786
- PMCID: PMC1930161
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2006.09.016
HIV-1 immunopathogenesis: how good interferon turns bad
Abstract
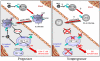
The hallmark of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is the progressive loss of CD4+ T cells that results from infection with human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1). Despite 25 years of AIDS research, questions remain concerning the mechanisms responsible for HIV-induced CD4+ T cell depletion. Here we briefly review the in vitro and in vivo literature concerning the protective role of interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) in HIV/AIDS. We then develop a laboratory- and clinically supported model of CD4+ T cell apoptosis in which either infectious or noninfectious HIV-1 induces the production of type I interferon by plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC). The interferon produced binds to its receptor on primary CD4+ T cells resulting in membrane expression of the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) death molecule. The binding of infectious or noninfectious HIV-1 to CD4 on these T cells results in expression of the TRAIL death receptor 5 (DR5), leading to the selective death of HIV-exposed CD4+ T cells.
Figures

References
-
- Li Q, Duan L, Estes JD, Ma ZM, Rourke T, Wang Y, Reilly C, Carlis J, Miller CJ, Haase AT. Peak SIV replication in resting memory CD4+ T cells depletes gut lamina propria CD4+ T cells. Nature. 2005;434:1148–52. - PubMed
-
- Mattapallil JJ, Douek DC, Hill B, Nishimura Y, Martin M, Roederer M. Massive infection and loss of memory CD4+ T cells in multiple tissues during acute SIV infection. Nature. 2005;434:1093–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

