Interactive effects of the mGlu5 receptor antagonist MPEP and the mGlu2/3 receptor antagonist LY341495 on nicotine self-administration and reward deficits associated with nicotine withdrawal in rats
- PMID: 17113075
- PMCID: PMC1803080
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.10.011
Interactive effects of the mGlu5 receptor antagonist MPEP and the mGlu2/3 receptor antagonist LY341495 on nicotine self-administration and reward deficits associated with nicotine withdrawal in rats
Abstract
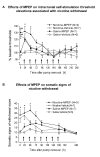
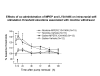
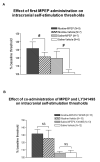
Stimulatory actions of nicotine on mesocorticolimbic dopamine transmission are partly mediated by nicotine-induced glutamate release acting on ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors. Because both presynaptic inhibitory mGlu2/3 and postsynaptic excitatory mGlu5 receptors provide potential targets for treatment of aspects of nicotine dependence, we examined interacting effects of mGlu5 (2-methyl-6-(phenylethynyl)-pyridine, MPEP) and mGlu2/3 (LY341495) receptor antagonists on nicotine self-administration and brain reward threshold elevations associated with spontaneous nicotine withdrawal in rats. We hypothesized that increasing glutamate transmission by blocking presynaptic inhibitory mGlu2/3 autoreceptors would antagonize MPEP-induced decreases in nicotine self-administration. We also hypothesized that blocking postsynaptic actions of glutamate on mGlu5 receptors would exacerbate nicotine withdrawal-induced reward deficits, and that this effect would be attenuated by co-administration of the mGlu2/3 receptor antagonist LY341495. MPEP selectively decreased nicotine, but not food, self-administration in rats. LY341495 slightly decreased both nicotine and food self-administration. Co-administration of LY341495 with MPEP attenuated the effectiveness of MPEP in decreasing nicotine intake, although MPEP was still effective. Spontaneous nicotine withdrawal induced somatic signs of withdrawal and reward threshold elevations indicating reward deficits. MPEP increased somatic signs and reward deficits in both nicotine- and saline-withdrawing rats. Thus, while mGlu5 receptor antagonists may be therapeutically useful in decreasing tobacco smoking, they worsen nicotine withdrawal. Co-administration of LY341495 reduced MPEP-induced reward deficits in both nicotine- and saline-withdrawing rats. Thus, increasing glutamate transmission via mGlu2/3 autoreceptor blockade reduces the effects of mGlu5 receptor blockade on nicotine self-administration and MPEP-induced exacerbation of brain reward deficits associated with nicotine withdrawal.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Group II metabotropic and alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionate (AMPA)/kainate glutamate receptors regulate the deficit in brain reward function associated with nicotine withdrawal in rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003 Sep;306(3):1068-76. doi: 10.1124/jpet.103.052027. Epub 2003 Jun 12. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003. PMID: 12805481
-
Metabotropic glutamate 2/3 receptor activation induced reward deficits but did not aggravate brain reward deficits associated with spontaneous nicotine withdrawal in rats.Biochem Pharmacol. 2007 Oct 15;74(8):1299-307. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.05.020. Epub 2007 May 29. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17601493
-
Antagonism at metabotropic glutamate 5 receptors inhibits nicotine- and cocaine-taking behaviours and prevents nicotine-triggered relapse to nicotine-seeking.Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Sep 19;499(1-2):121-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.07.056. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15363959
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists: novel therapeutics for nicotine dependence and depression?Biol Psychiatry. 2007 Jan 1;61(1):17-22. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.03.053. Epub 2006 Jul 28. Biol Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 16876138 Review.
-
mGlu5 receptor antagonists: a novel class of anxiolytics?Drug News Perspect. 2004 May;17(4):251-7. doi: 10.1358/dnp.2004.17.4.829052. Drug News Perspect. 2004. PMID: 15334174 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of allosteric modulators of GPCRs for treatment of CNS disorders.Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Jan;61:55-71. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2013.09.013. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Neurobiol Dis. 2014. PMID: 24076101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 as a Target for the Treatment of Depression and Smoking: Robust Preclinical Data but Inconclusive Clinical Efficacy.Biol Psychiatry. 2018 Jun 1;83(11):955-962. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Biol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29628194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of the beta-lactam antibiotic ceftriaxone on nicotine withdrawal and nicotine-induced reinstatement of preference in mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Aug;228(3):419-26. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3047-3. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 23503685 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of the mGluR5 receptor antagonist 6-methyl-2-(phenylethynyl)-pyridine (MPEP) on behavioural responses to nicotine.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010 Jul;211(1):33-42. doi: 10.1007/s00213-010-1868-x. Epub 2010 Apr 27. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010. PMID: 20422403 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in mechanisms underlying reinstatement of cigarette smoke extract- and nicotine-seeking behavior in rats.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Jan 1;162:107846. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.107846. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 31704271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoki T, Narita M, Shibasaki M, Suzuki T. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 localized in the limbic forebrain is critical for the development of morphine-induced rewarding effect in mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004;20:1633–1638. - PubMed
-
- Bespalov AY, Dravolina OA, Sukhanov I, Zakharova E, Blokhina E, Zvartau E, Danysz W, van Heeke G, Markou A. Metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR5) antagonist MPEP attenuated cue- and schedule-induced reinstatement of nicotine self-administration behavior in rats. Neuropharmacology. 2005;49(Suppl 1):167–178. - PubMed
-
- Caine B, Koob GF. In: Intravenous drug self-administration techniques in animals, in: Behavoural neruroscience: a practical approach. Sahgal A, editor. IRL Press; Oxford: 1993. pp. 117–143.
-
- Chaki S, Yoshikawa R, Hirota S, Shimazaki T, Maeda M, Kawashima N, Yoshimizu T, Yasuhara A, Sakagami K, Okuyama S, Nakanishi S, Nakazato A. MGS0039: a potent and selective group II metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist with antidepressant-like activity. Neuropharmacology. 2004;46:457–467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

