Nucleophosmin and human cancer
- PMID: 17113241
- PMCID: PMC1853269
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cdp.2006.10.008
Nucleophosmin and human cancer
Abstract
Nucleophosmin (NPM) is a nucleolar phosphoprotein that shuttles between the nucleus and cytoplasm during the cell cycle. NPM has several interacting partners and diverse cellular functions, including the processing of ribosomal RNA, centrosome duplication and the control of cellular processes to ensure genomic stability. Subcellular localization of NPM appears to be strongly correlated with NPM functions and cell proliferation. NPM is phosphorylated mainly at its central acidic domain by several upstream kinases, and its phosphorylation appears to be involved in regulating its functions in ribosome biogenesis and centrosome duplication. Recent studies suggest that NPM may act as a licensing factor to maintain proper centrosome duplication and that the Ran/CRM1 nucleocytoplasmic complex regulates local trafficking of NPM to centrosomes by interacting through its nuclear export sequence motif. Here, we provide a brief overview of NPM functions and its roles in human carcinogenesis, and discuss our recent findings related to the potential mechanisms underlying its regulation of centrosome duplication.
Figures

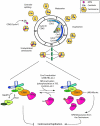
References
-
- Yung BY, Busch H, Chan PK. Translocation of nucleolar phosphoprotein B23 (37 kDa/pI 5.1) induced by selective inhibitors of ribosome synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985;826:167–173. - PubMed
-
- Feuerstein N, Mond JJ. “Numatrin,” a nuclear matrix protein associated with induction of proliferation in B lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:11389–11397. - PubMed
-
- Chang JH, Olson MO. Structure of the gene for rat nucleolar protein B23. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:18227–18233. - PubMed
-
- Wang D, Baumann A, Szebeni A, Olson MO. The nucleic acid binding activity of nucleolar protein B23.1 resides in its carboxyl-terminal end. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:30994–30998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

