The S. cerevisiae Rrm3p DNA helicase moves with the replication fork and affects replication of all yeast chromosomes
- PMID: 17114583
- PMCID: PMC1635146
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1478906
The S. cerevisiae Rrm3p DNA helicase moves with the replication fork and affects replication of all yeast chromosomes
Abstract
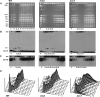
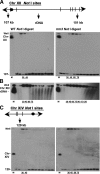
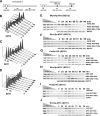
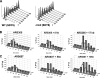
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA helicase Rrm3p is needed for normal fork progression through >1000 discrete sites scattered throughout the genome. Here we show that replication of all yeast chromosomes was markedly delayed in rrm3 cells. Delayed replication was seen even in a region that lacks any predicted Rrm3p-dependent sites. Based on the pattern of replication intermediates in two-dimensional gels, the rate of fork movement in rrm3 cells appeared similar to wild-type except at known Rrm3p-dependent sites. These data suggest that although Rrm3p has a global role in DNA replication, its activity is needed only or primarily at specific, difficult-to-replicate sites. By the criterion of chromatin immunoprecipitation, Rrm3p was associated with both Rrm3p-dependent and -independent sites, and moved with the replication fork through both. In addition, Rrm3p interacted with Pol2p, the catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase epsilon, in vivo. Thus, rather than being recruited to its sites of action when replication forks stall at these sites, Rrm3p is likely a component of the replication fork apparatus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Tof1p-Csm3p protein complex counteracts the Rrm3p helicase to control replication termination of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jan 24;103(4):897-902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506540103. Epub 2006 Jan 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16418273 Free PMC article.
-
The Saccharomyces Pif1p DNA helicase and the highly related Rrm3p have opposite effects on replication fork progression in ribosomal DNA.Cell. 2000 Feb 18;100(4):479-89. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80683-2. Cell. 2000. PMID: 10693764
-
Saccharomyces Rrm3p, a 5' to 3' DNA helicase that promotes replication fork progression through telomeric and subtelomeric DNA.Genes Dev. 2002 Jun 1;16(11):1383-96. doi: 10.1101/gad.982902. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 12050116 Free PMC article.
-
The MCM helicase: linking checkpoints to the replication fork.Biochem Soc Trans. 2008 Feb;36(Pt 1):114-9. doi: 10.1042/BST0360114. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008. PMID: 18208397 Review.
-
Yeast Genome Maintenance by the Multifunctional PIF1 DNA Helicase Family.Genes (Basel). 2020 Feb 20;11(2):224. doi: 10.3390/genes11020224. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32093266 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-range heterochromatin association is mediated by silencing and double-strand DNA break repair proteins.J Cell Biol. 2013 Jun 10;201(6):809-26. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201211105. Epub 2013 Jun 3. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23733345 Free PMC article.
-
TbPIF1, a Trypanosoma brucei mitochondrial DNA helicase, is essential for kinetoplast minicircle replication.J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 5;285(10):7056-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.084038. Epub 2009 Dec 30. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20042610 Free PMC article.
-
Pif1 family helicases promote mutation avoidance during DNA replication.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Dec 9;50(22):12844-12855. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1127. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36533450 Free PMC article.
-
Dbf4-Dependent Kinase: DDK-ated to post-initiation events in DNA replication.Cell Cycle. 2021 Nov;20(22):2348-2360. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1986999. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 34662256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Absence of Non-histone Protein Complexes at Natural Chromosomal Pause Sites Results in Reduced Replication Pausing in Aging Yeast Cells.Cell Rep. 2016 Nov 8;17(7):1747-1754. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.10.050. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27829146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alcasabas, A., Osborn, A., Bachant, J., Hu, F., Werler, P., Bousset, K., Furuya, K., Diffley, J., Carr, A., Elledge, S. Mrc1 transduces signals of DNA replication stress to activate Rad53. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001;3:958–965. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio, O.M., Weinstein, D.M., Bell, S.P. Components and dynamics of DNA replication complexes in S. cerevisiae: Redistribution of MCM proteins and Cdc45p during S phase. Cell. 1997;91:59–69. - PubMed
-
- Barry, J., Alberts, B. A role for two DNA helicases in the replication of T4 bacteriophage DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:33063–33068. - PubMed
-
- Bedinger, P., Hochstrasser, M., Jongeneel, C., Alberts, B. Properties of the T4 bacteriophage DNA replication apparatus: The T4 dda DNA helicase is required to pass a bound RNA polymerase molecule. Cell. 1983;34:115–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
