Smad4 is dispensable for normal pancreas development yet critical in progression and tumor biology of pancreas cancer
- PMID: 17114584
- PMCID: PMC1635148
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1478706
Smad4 is dispensable for normal pancreas development yet critical in progression and tumor biology of pancreas cancer
Abstract
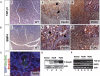
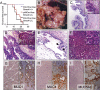
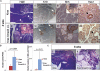
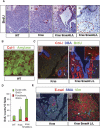
SMAD4 is inactivated in the majority of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDAC) with concurrent mutational inactivation of the INK4A/ARF tumor suppressor locus and activation of the KRAS oncogene. Here, using genetically engineered mice, we determined the impact of SMAD4 deficiency on the development of the pancreas and on the initiation and/or progression of PDAC-alone or in combination with PDAC--relevant mutations. Selective SMAD4 deletion in the pancreatic epithelium had no discernable impact on pancreatic development or physiology. However, when combined with the activated KRAS(G12D) allele, SMAD4 deficiency enabled rapid progression of KRAS(G12D)-initiated neoplasms. While KRAS(G12D) alone elicited premalignant pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) that progressed slowly to carcinoma, the combination of KRAS(G12D) and SMAD4 deficiency resulted in the rapid development of tumors resembling intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasia (IPMN), a precursor to PDAC in humans. SMAD4 deficiency also accelerated PDAC development of KRAS(G12D) INK4A/ARF heterozygous mice and altered the tumor phenotype; while tumors with intact SMAD4 frequently exhibited epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), PDAC null for SMAD4 retained a differentiated histopathology with increased expression of epithelial markers. SMAD4 status in PDAC cell lines was associated with differential responses to transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) in vitro with a subset of SMAD4 wild-type lines showing prominent TGF-beta-induced proliferation and migration. These results provide genetic confirmation that SMAD4 is a PDAC tumor suppressor, functioning to block the progression of KRAS(G12D)-initiated neoplasms, whereas in a subset of advanced tumors, intact SMAD4 facilitates EMT and TGF-beta-dependent growth.
Figures


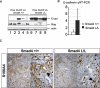
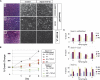
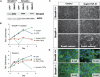
Comment in
-
The molecular pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer: clarifying a complex circuitry.Genes Dev. 2006 Nov 15;20(22):3049-53. doi: 10.1101/gad.1501106. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 17114578 No abstract available.
References
-
- Adsay, N.V., Merati, K., Basturk, O., Iacobuzio-Donahue, C., Levi, E., Cheng, J.D., Sarkar, F.H., Hruban, R.H., Klimstra, D.S. Pathologically and biologically distinct types of epithelium in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: Delineation of an ‘intestinal’ pathway of carcinogenesis in the pancreas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2004;28:839–848. - PubMed
-
- Apte, M.V., Park, S., Phillips, P.A., Santucci, N., Goldstein, D., Kumar, R.K., Ramm, G.A., Buchler, M., Friess, H., McCarroll, J.A., et al. Desmoplastic reaction in pancreatic cancer: Role of pancreatic stellate cells. Pancreas. 2004;29:179–187. - PubMed
-
- Bardeesy, N., Sinha, M., Hezel, A.F., Signoretti, S., Hathaway, N.A., Sharpless, N.E., Loda, M., Carrasco, D.R., DePinho, R.A. Loss of the Lkb1 tumour suppressor provokes intestinal polyposis but resistance to transformation. Nature. 2002b;419:162–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
