Effects of HCV treatment on cytokine expression during HCV/HIV coinfection
- PMID: 17115902
- PMCID: PMC4113398
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2006.26.834
Effects of HCV treatment on cytokine expression during HCV/HIV coinfection
Abstract
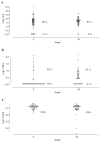
There is growing evidence that cytokine expression is linked to hepatitis C virus (HCV) pathogenesis and treatment response rates among HCV-monoinfected persons. However, because of the profound effects of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) coinfection on HCV, it is not clear if these observations are also true for HCV/HIV-coinfected individuals. Serum expression of the proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-8 (IL-8) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and the fibrogenic cytokine transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) were measured in HCV/HIV-coinfected persons at baseline and at week 24 of HCV therapy. Higher levels of IL-8 and TGF-beta were demonstrated among nonwhite subjects at baseline. Increases in TNF-alpha and IL-8 expression were found at week 24 of HCV therapy, suggesting that enhanced proinflammatory cytokine production may occur during HCV treatment. However, cytokine levels were not predictive of HCV virologic, biochemical, or histologic response. Although previous studies conducted among HCV-monoinfected individuals have suggested that cytokine levels could predict the virologic response to therapy, no such associations were observed among HCV/HIV-coinfected persons, suggesting that they may respond differently to treatment than do their HCV-monoinfected counterparts.
Figures
References
-
- Heydtmann H, Shields P, McCaughan G, Adams D. Cytokines and chemokines in the immune response to hepatitis C infection. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2001;14:279–287. - PubMed
-
- Jacobson-Brown P, Neuman M. Immunopathogenesis of hepatitis C viral infection: Th1/Th2 responses and the role of cytokines. Clin Biochem. 2001;34:167–171. - PubMed
-
- Napoli J, Bishop A, McGuinness P, Painter D, McCaughan G. Progressive liver injury in chronic hepatitis C infection correlates with increased intrahepatic expression of Th1-associated cytokines. Hepatology. 1996;24:759–765. - PubMed
-
- Fukuda R, Ishimura N, Ishihara S, Chowdhury A, Morlyama N, Nogami C, Miyake T, Niigaki M, Tokuda A, Satoh S, Sakai S, Akagi S, Watanabe M, Fukumoto S. Intrahepatic expression of proinflammatory cytokine mRNAs and interferon efficacy in chronic hepatitis C. Liver. 1996;16:390–399. - PubMed
-
- Neuman M, Benhamou J, Bourliere M, Ibrahim A, Malkiewicz I, Asselah T, Martinot-Peignoux M, Shear NH, Katz GG, Akremi R, Benali S, Boyer N, Lecomte L, Le Breton V, Le Guludec G, Marcellin P. Serum tumour necrosis factor-α and transforming growth factor-b levels in chronic hepatitis C patients are immunomodulated by therapy. Cytokine. 2002;17:108–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

