Substitution of phenylephrine for pseudoephedrine as a nasal decongeststant. An illogical way to control methamphetamine abuse
- PMID: 17116124
- PMCID: PMC2000711
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2006.02833.x
Substitution of phenylephrine for pseudoephedrine as a nasal decongeststant. An illogical way to control methamphetamine abuse
Abstract
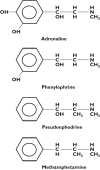
The aim of this review was to investigate the rationale for replacing the nasal decongestant pseudoephedrine (PDE) with phenylephrine (PE) as a means of controlling the illicit production of methamphetamine. A literature search was conducted in electronic databases and use of textbooks. Restrictions have been placed on the sale of PDE in the USA in an attempt to control the illicit production of methamphetamine. This has caused a switch from PDE to PE in many common cold and cough medicines. PE is a poor substitute for PDE as an orally administered decongestant as it is extensively metabolized in the gut and its efficacy as a decongestant is unproven. Both PDE and PE have a good safety record, but the efficacy of PDE as a nasal decongestant is supported by clinical trials. Studies in the USA indicate that restricting the sale of PDE to the public as a medicine has had little impact on the morbidity and number of arrests associated with methamphetamine abuse. Restricting the sale of PDE in order to control the illicit production of methamphetamine will deprive the public of a safe and effective nasal decongestant and force the pharmaceutical industry to replace PDE with PE, which may be an ineffective decongestant. Restrictions on sales of PDE to the public may not reduce the problems associated with methamphetamine abuse.
Figures
Comment in
-
Efficacy of phenylephrine.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2007 Oct;64(4):555-6; author reply 557. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.02935.x. Epub 2007 Jul 4. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17610531 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- UK OTC Directory, Treatments for Common Ailments (PAGB) London: Communications International Group; 20052006.
-
- Aviado DM, Jr, Wnuck AL, De Beer ES. A comparative study of nasal de-congestion by sympathomimetic drugs. Arch Otolaryngol. 1959;69:598–605. - PubMed
-
- Meadows M. FDA issues public health advisory on phenylpropanolamine in drug products. FDA Consum. 2001;35:9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical