Steady-state pharmacokinetics of micafungin and voriconazole after separate and concomitant dosing in healthy adults
- PMID: 17116670
- PMCID: PMC1797737
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00673-06
Steady-state pharmacokinetics of micafungin and voriconazole after separate and concomitant dosing in healthy adults
Abstract
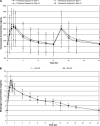
We assessed the pharmacokinetics and interactions of steady-state micafungin (Mycamine) or placebo with steady-state voriconazole in 35 volunteers. The 90% confidence intervals around the least-squares mean ratios for micafungin pharmacokinetic parameters and placebo-corrected voriconazole pharmacokinetic parameters were within the 80%-to-125% limits, indicating an absence of drug interaction.
Figures
References
-
- Astellas Pharma US, Inc. April 2005. Mycamine (micafungin sodium) for injection: full U.S. prescribing information. Astellas Pharma US, Inc., Deerfield, IL.
-
- Dowell, J. A., J. Schranz, A. Baruch, and G. Foster. 2005. Safety and pharmacokinetics of coadministered voriconazole and anidulafungin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 45:1373-1382. - PubMed
-
- Hatano, K., Y. Morishita, T. Nakai, and F. Ikeda. 2002. Antifungal mechanism of FK463 against Candida albicans and Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Antibiot. 55:219-222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources