Power spectra reveal the influence of stochasticity on nonlinear population dynamics
- PMID: 17116860
- PMCID: PMC1693752
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0608571103
Power spectra reveal the influence of stochasticity on nonlinear population dynamics
Abstract
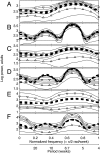
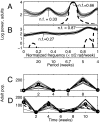
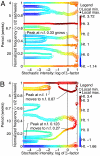
Stochasticity alters the nonlinear dynamics of inherently cycling populations. The power spectrum can describe and explain the impacts of stochasticity. We fitted models to short observed time series of flour beetle populations in the frequency domain, then used a well fitting stochastic mechanistic model to generate detailed predictions of population spectra. Some predicted spectral peaks represent periodic phenomena induced or modified by stochasticity and were experimentally confirmed. For one experimental treatment, linearization theory explained that these peaks represent overcompensatory decay of deviations from deterministic oscillation. In another treatment, stochasticity caused frequent directional phase shifting around a cyclic attractor. This directional phase shifting was not explained by linearization theory and modified the periodicity of the system. If field systems exhibit directional phase shifting, then changing the intensity of demographic or environmental noise while holding constant the structure of the noise can change the main frequency of population fluctuations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Revealing the ghost in the machine: using spectral analysis to understand the influence of noise on population dynamics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Dec 5;103(49):18387-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0609323103. Epub 2006 Nov 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17130444 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

