Social buffering: relief from stress and anxiety
- PMID: 17118934
- PMCID: PMC1764848
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2006.1941
Social buffering: relief from stress and anxiety
Abstract
Communication is essential to members of a society not only for the expression of personal information, but also for the protection from environmental threats. Highly social mammals have a distinct characteristic: when conspecific animals are together, they show a better recovery from experiences of distress. This phenomenon, termed 'social buffering', has been found in rodents, birds, non-human primates and also in humans. This paper reviews classical findings on social buffering and focuses, in particular, on social buffering effects in relation to neuroendocrine stress responses. The social cues that transmit social buffering signals, the neural mechanisms of social buffering and a partner's efficacy with respect to social buffering are also detailed. Social contact appears to have a very positive influence on the psychological and the physiological aspects of social animals, including human beings. Research leading towards further understanding of the mechanisms of social buffering could provide alternative medical treatments based on the natural, individual characteristics of social animals, which could improve the quality of life.
Figures
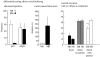
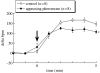
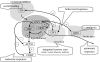
Similar articles
-
Anxiety-like behavior and neuropeptide receptor expression in male and female prairie voles: The effects of stress and social buffering.Behav Brain Res. 2018 Apr 16;342:70-78. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.01.015. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Behav Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29355675 Free PMC article.
-
Social Buffering as a Tool for Improving Rodent Welfare.J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2022 Jan 1;61(1):5-14. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-21-000006. Epub 2021 Dec 16. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 34915978 Free PMC article.
-
Partner's stress status influences social buffering effects in rats.Behav Neurosci. 2004 Aug;118(4):798-804. doi: 10.1037/0735-7044.118.4.798. Behav Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15301605
-
Convergent neuroendocrine mechanisms of social buffering and stress contagion.Horm Behav. 2021 Mar;129:104933. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2021.104933. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Horm Behav. 2021. PMID: 33465346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Social buffering of stress responses in nonhuman primates: Maternal regulation of the development of emotional regulatory brain circuits.Soc Neurosci. 2015;10(5):512-26. doi: 10.1080/17470919.2015.1087426. Epub 2015 Sep 17. Soc Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26324227 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intranasal oxytocin compensates for estrus cycle-specific reduction of conditioned safety memory in rats: Implications for psychiatric disorders.Neurobiol Stress. 2021 Mar 10;14:100313. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2021.100313. eCollection 2021 May. Neurobiol Stress. 2021. PMID: 33778132 Free PMC article.
-
Attachment style moderates partner presence effects on pain: a laser-evoked potentials study.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2015 Aug;10(8):1030-7. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsu156. Epub 2015 Jan 1. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25556212 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal buffering of fear-potentiated startle in children and adolescents with trauma exposure.Soc Neurosci. 2017 Feb;12(1):22-31. doi: 10.1080/17470919.2016.1164244. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Soc Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27056324 Free PMC article.
-
Improved behavioral indices of welfare in continuous compared to intermittent pair-housing in adult female rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta).Am J Primatol. 2020 Oct;82(10):e23189. doi: 10.1002/ajp.23189. Epub 2020 Sep 5. Am J Primatol. 2020. PMID: 32890432 Free PMC article.
-
Reunion behavior after social separation is associated with enhanced HPA recovery in young marmoset monkeys.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015 Jul;57:93-101. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2015.03.019. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25900596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adels L.E, Leon M, Wiener S.G, Smith M.S. Endocrine response to acute cold exposure by lactating and non-lactating Norway rats. Physiol. Behav. 1986;36:179–181. doi:10.1016/0031-9384(86)90093-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ågren G, Lundeberg T. Social stress blocks energy conservation in rats exposed to an oxytocin-injected cagemate. Neuroreport. 2002;13:1415–1419. - PubMed
-
- Ågren G, Uvnas-Moberg K, Lundeberg T. Olfactory cues from an oxytocin-injected male rat can induce anti-nociception in its cagemates. Neuroreport. 1997;8:3073–3076. - PubMed
-
- Altemus M, Deuster P.A, Galliven E, Carter C.S, Gold P.W. Suppression of hypothalmic–pituitary–adrenal axis responses to stress in lactating women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995;80:2954–2959. doi:10.1210/jc.80.10.2954 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amico J.A, Johnston J.M, Vagnucci A.H. Suckling-induced attenuation of plasma cortisol concentrations in postpartum lactating women. Endocr. Res. 1994;20:79–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

