A genomic island of the pathogen Leptospira interrogans serovar Lai can excise from its chromosome
- PMID: 17118975
- PMCID: PMC1828511
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01067-06
A genomic island of the pathogen Leptospira interrogans serovar Lai can excise from its chromosome
Abstract
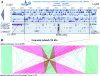
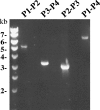
An examination of the two Leptospira interrogans genomes sequenced so far reveals few genetic differences, including an extra DNA region, 54 kb in length, in L. interrogans serovar Lai. This locus contains 103 predicted coding sequences that are absent from the genome of L. interrogans serovar Copenhageni, of which only 20% had significant BLASTP hits in GenBank. By analyzing the L. interrogans serovar Lai genome by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, we also found that this 54-kb DNA fragment exists as a circular plasmid. This was confirmed by amplification of a DNA fragment corresponding to that of the predicted fragment if this region excised from the chromosome and its left and right ends joined together. In addition, cloning of the putative rep gene of this DNA region was responsible for autonomous replication in Leptospira spp., therefore generating a new Escherichia coli-Leptospira sp. shuttle vector. Taken together, our results show that this genomic island can excise from the chromosome and form a replicative plasmid. Analysis of the distribution of this genomic island revealed that highly related sequences exist in other L. interrogans virulent strains. This genomic island, containing a high proportion of novel genes, may have an important role in spreading genes, including virulence factors, among bacterial populations.
Figures

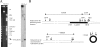
Similar articles
-
Identification of three extra-chromosomal replicons in Leptospira pathogenic strain and development of new shuttle vectors.BMC Genomics. 2015 Feb 15;16(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1321-y. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25887950 Free PMC article.
-
Physical and genetic maps of the Leptospira interrogans serovar icterohaemorrhagiae strain Ictero no.1 chromosome and sequencing of a 19-kb region of the genome containing the 5S rRNA gene.Gene. 1998 Jul 17;215(1):37-45. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(98)00277-7. Gene. 1998. PMID: 9666070
-
Re-characterization of an extrachromosomal circular plasmid in the pathogenic Leptospira interrogans serovar Lai strain 56601.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2014 Jul;46(7):605-11. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmu033. Epub 2014 May 29. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2014. PMID: 24874103
-
Genetic diversity among major endemic strains of Leptospira interrogans in China.BMC Genomics. 2007 Jul 1;8:204. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-204. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17603913 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic techniques for identification of Leptospira strains.Pathol Biol (Paris). 1993 Dec;41(10):943-50. Pathol Biol (Paris). 1993. PMID: 8159475 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of three extra-chromosomal replicons in Leptospira pathogenic strain and development of new shuttle vectors.BMC Genomics. 2015 Feb 15;16(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1321-y. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25887950 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of Plasmids in Distinct Leptospira Pathogenic Species.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015 Nov 10;9(11):e0004220. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004220. eCollection 2015 Nov. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015. PMID: 26555137 Free PMC article.
-
A replicative plasmid vector allows efficient complementation of pathogenic Leptospira strains.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 May 1;81(9):3176-81. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00173-15. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25724960 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Variability among Field Isolates and Laboratory-Adapted Strains of Leptospira borgpetersenii Serovar Hardjo.Int J Microbiol. 2018 May 22;2018:2137036. doi: 10.1155/2018/2137036. eCollection 2018. Int J Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29951097 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative proteogenomic analysis of the Leptospira interrogans virulence-attenuated strain IPAV against the pathogenic strain 56601.Cell Res. 2011 Aug;21(8):1210-29. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.46. Epub 2011 Mar 22. Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21423275 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Canchaya, C., G. Fournous, and H. Brussow. 2004. The impact of prophages on bacterial chromosomes. Mol. Microbiol. 53:9-18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

