Interdigitated paralemniscal and lemniscal pathways in the mouse barrel cortex
- PMID: 17121453
- PMCID: PMC1637129
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040382
Interdigitated paralemniscal and lemniscal pathways in the mouse barrel cortex
Erratum in
- PLoS Biol. 2007 Jan;5(1):e28
Abstract
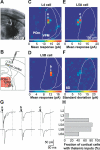
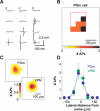
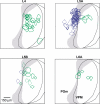
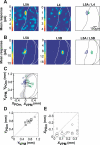
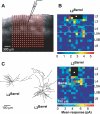
Primary sensory cortical areas receive information through multiple thalamic channels. In the rodent whisker system, lemniscal and paralemniscal thalamocortical projections, from the ventral posteromedial nucleus (VPM) and posterior medial nucleus (POm) respectively, carry distinct types of sensory information to cortex. Little is known about how these separate streams of activity are parsed and integrated within the neocortical microcircuit. We used quantitative laser scanning photostimulation to probe the organization of functional thalamocortical and ascending intracortical projections in the mouse barrel cortex. To map the thalamocortical projections, we recorded from neocortical excitatory neurons while stimulating VPM or POm. Neurons in layers (L)4, L5, and L6A received dense input from thalamus (L4, L5B, and L6A from VPM; and L5A from POm), whereas L2/3 neurons rarely received thalamic input. We further mapped the lemniscal and paralemniscal circuits from L4 and L5A to L2/3. Lemniscal L4 neurons targeted L3 within a column. Paralemniscal L5A neurons targeted a superficial band (thickness, 60 mum) of neurons immediately below L1, defining a functionally distinct L2 in the mouse barrel cortex. L2 neurons received input from lemniscal L3 cells and paralemniscal L5A cells spread over multiple columns. Our data indicate that lemniscal and paralemniscal information is segregated into interdigitated cortical layers.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Comment in
-
Shedding light on local organizational principles in the primary sensory cortex.PLoS Biol. 2006 Dec;4(12):e420. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040420. Epub 2006 Nov 21. PLoS Biol. 2006. PMID: 20076507 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Woolsey TA, Van der Loos H. The structural organization of layer IV in the somatosensory region (S1) of mouse cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1970;17:205–242. - PubMed
-
- Agmon A, Connors BW. Thalamocortical responses of mouse somatosensory (barrel) cortex in vitro. Neuroscience. 1991;41:365–379. - PubMed
-
- Rice FL. Comparative aspects of barrel structure and development. In: Jones EG, Diamond IT, editors. The barrel cortex of rodents. New York: Plenum Press; 1995. pp. 1–76.
-
- Welker C. Microelectrode delineation of fine grain somatotopic organization of (SmI) cerebral neocortex in albino rat. Brain Res. 1971;26:259–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

