Determining human immunodeficiency virus coreceptor use in a clinical setting: degree of correlation between two phenotypic assays and a bioinformatic model
- PMID: 17122004
- PMCID: PMC1829003
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01118-06
Determining human immunodeficiency virus coreceptor use in a clinical setting: degree of correlation between two phenotypic assays and a bioinformatic model
Abstract
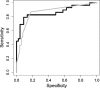
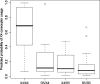
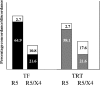
Two recombinant phenotypic assays for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) coreceptor usage and an HIV envelope genotypic predictor were employed on a set of clinically derived HIV type 1 (HIV-1) samples in order to evaluate the concordance between measures. Previously genotyped HIV-1 samples derived from antiretroviral-naïve individuals were tested for coreceptor usage using two independent phenotyping methods. Phenotypes were determined by validated recombinant assays that incorporate either an approximately 2,500-bp ("Trofile" assay) or an approximately 900-bp (TRT assay) fragment of the HIV envelope gp120. Population-based HIV envelope V3 loop sequences ( approximately 105 bp) were derived by automated sequence analysis. Genotypic coreceptor predictions were performed using a support vector machine model trained on a separate genotype-Trofile phenotype data set. HIV coreceptor usage was obtained from both phenotypic assays for 74 samples, with an overall 85.1% concordance. There was no evidence of a difference in sensitivity between the two phenotypic assays. A bioinformatic algorithm based on a support vector machine using HIV V3 genotype data was able to achieve 86.5% and 79.7% concordance with the Trofile and TRT assays, respectively, approaching the degree of agreement between the two phenotype assays. In most cases, the phenotype assays and the bioinformatic approach gave similar results. However, in cases where there were differences in the tropism results, it was not clear which of the assays was "correct." X4 (CXCR4-using) minority species in clinically derived samples likely complicate the interpretation of both phenotypic and genotypic assessments of HIV tropism.
Figures

References
-
- Brumme, Z. L., W. W. Y. Dong, B. Yip, B. Wynhoven, N. G. Hoffman, R. Swanstrom, M. A. Jensen, J. I. Mullins, R. S. Hogg, J. S. G. Montaner, and P. R. Harrigan. 2004. Clinical and immunological impact of HIV envelope V3 sequence variation after starting initial antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 18:F1-F9. - PubMed
-
- Brumme, Z. L., J. Goodrich, H. B. Mayer, C. J. Brumme, B. M. Henrick, B. Wynhoven, J. J. Asselin, P. K. Cheung, R. S. Hogg, J. S. G. Montaner, and P. R. Harrigan. 2005. Molecular and clinical epidemiology of CXCR4-using HIV-1 in a large population of antiretroviral-naïve individuals. J. Infect. Dis. 192:466-474. - PubMed
-
- Capon, D., and C. J. Petropoulos. November. 1998. Compositions and methods for determining anti-viral drug susceptibility and resistance and anti-viral drug screening. U.S. patent 5,837,464.
-
- Coakley, E., C. J. Petropoulos, and J. M. Whitcomb. 2005. Assessing chemokine co-receptor usage in HIV. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 18:9-15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

